Contents
Characteristics of aronia (Aronia melanocarpa)
What is an aronia?
Common English name: Aronia, black chokeberry, aronia berries (based on the fruit).
Scientific name: Aronia melanocarpa (Michx.) Elliott. Synonym: Photinia melanocarpa.
* See: Aronia in other languages
Family: Rosaceae -rose family
Habitat: It is a plant native to eastern North American continent and widespread in Russia and Eastern Europe after World War II, when it is grown as a medicinal plant.
It is a plant that grows well with plenty of sun and semi – shade; and in wet or swampy soils. It can tolerate different soil types: sand, gravel, clay, drought and humidity.
It is resistant to frost up to -25 º C and pollution of urban gardens very hardy and vigorous plant. In very dry areas usually develop iron chlorosis (yellowing of leaves due to iron deficiency). It does not tolerate calcareous soils.
Ideal conditions for growth: moderate watering, sun exposure or partial shade, clay soil, acid soil and good drainage. When conditions are favorable, growth is fast and can easily form large thickets.
For his resistance to adverse climate, its adaptability to all kinds of terrain and beauty of bright green leaves that are tinged with reddish-yellow in autumn, this shrub is an excellent ornamental plant gardens.
Botanical description of aronia
Drawing of the plant
The word aronia comprises a genus belonging to the Rosaceae family, which includes a large number of plants.
Specifically, The marketed aronia species is black aronia (Aronia melanocarpa), because in America, where the plant is native, there is also a red chokeberry (Aronia arbutifolia, and a purple aronia (Aronia prunifolia), which is a hybrid of the two.
Black aronia is a deciduous shrub that can measure between 2 and 2.5 meters high, and its top can be of a similar diameter between 2 and 3 meters wide, so the shrub has a rounded appearance.
It has several woody stems, reddish and grow as sprouts. These stems grow from erect rhizome and may may form small colonies of very dense shrub foliage.
Its leaves are petiolate, simple, glabrous (smooth and shiny). They measure between 3 and 8 cm long by 1.5 to 3 cm wide, oblong and serrated on the sides. Unlike red chokeberry (Aronia arbutifolia) a plant with very similar characteristics, black aronia has no pubescence (hair) or on the back of its leaves or on the stem.
The hairless black aronia foliage is bright and shiny green in the summer and dyed orange and yellow in autumn before leaves fall.
The inflorescences of the plant are slightly-white pink flowers, growing in clusters of about 4 inches wide. These clusters can be very numerous, and contain 7 to 10 flowers each.
They bloom in May, though some later varieties do in June. Flowers are actinomorphic and dialipetalous, consisting of 5 petals and 5 sepals; hermaphrodites, with size from 0.8 to 1.2 centimeters in diameter. Pollinated by insects, they usually attract butterflies and bees.
The fruit is a berry, round and small, wit a size between 1 and 1.5 cm in diameter. They come in groups 7-10, hanging from the leaf axils. The bright black-purple color of the fruits gives the common name to the bush. They mature in late autumn.
What does aronia fruit contain?
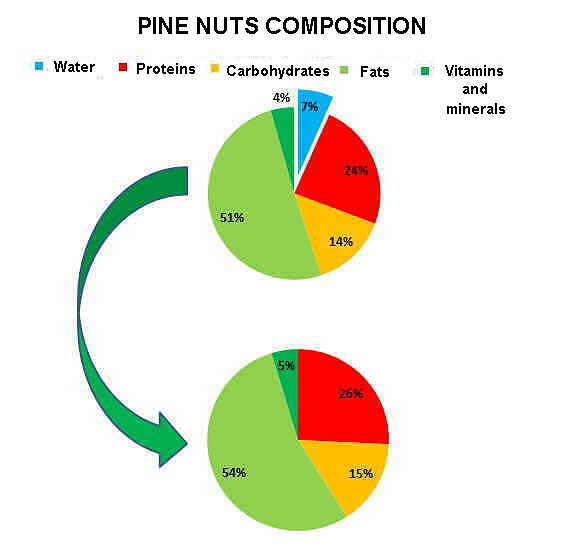
The fruit of aronia is valuable nutritionally because of their composition:
- It is a low calorie fruit, as it only reaches 50kcal per 100g
- It contains soluble fiber pectin, which makes it an ideal fruit for making jam.
- With a low amount of sugar (9g per 100g of food), which makes it a suitable and recommended fruit for diabetics and thinning people .
- It has a very low, almost negligible content in fat (0.5g per 100g), and a low intake of protein, 1.4g per 100g.
- What really stands out about this fruit is its high antioxidant power, valued at 16,062 points ORAC scale (very high value); and each rich in flavonoids (zeaxanthin, lutein, quinic acid and anthocyanins). Its value exceeds that of blueberries and other fruit, reason why it is increasing the interest in this plant for its medicinal purposes.
It also contains tannins, which give this fruit a very harsh and astringent taste. Therefore it is recommended to take this fruit juice, because it has better flavor properties.
*More information: Table of nutritional composition of aronia.
Varieties of aronia
Different varieties of aronias differ depending on their use, mainly for ornamental or because of their use:
- Aronia Autumn Magic: dwarf variety grown for ornamental purposes in compact form. It produces good fruits and has glossy leaves. As its name suggests, in the fall it becomes very vivid reddish colored.
- Aronia Morton: dense variety of low aronia (90-120 cm high) (60-90 cm wide). Deciduous, green, with wider leaves than common aronia. This variety was selected by the Organization Morton Arboretum in Illinois (hence the name of the variety). The bush was presented in the Introduction program of Chicagoland Grows and this plant is currently marketed under the name of IROQUOIS BEAUTY.
- Aronia Viking range: European variety of medium size, between 1 and 1.5 meters in height and width. Bushy glabrous shrub with shiny leaves, black large-sized fruits. Aimed at obtaining results. Along with the Nero variety, they are the most sold.
- Nero or Nero Aronia: European variety fruits characterized by having double the size of the common aronia and because of its high vitamin C content, providing 30 mg per 100g of food (twice that of aronias in other species). Along with Viking range, it is the main marketed.
![]() More information on aronia.
More information on aronia.