Contents
How to grow Barbados cherry
Acerola plant characteristics
– Acerola (Malpighia emarginata) is an evergreen shrub of the Malpighiaceae family.
– Semi-postrated or erect shrub, up to 3m. tall with a dense foliage.
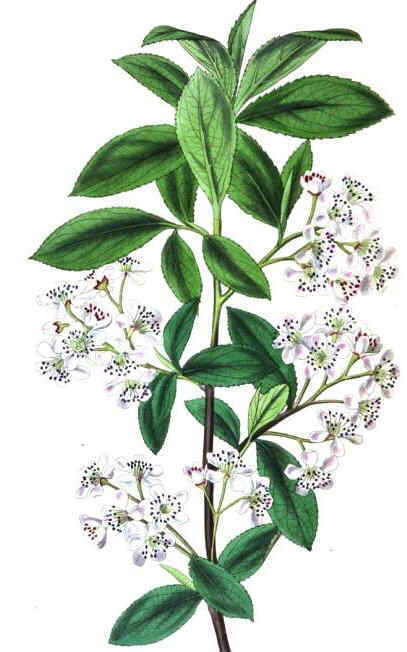
– Stalked, elliptical or oval leaves with obtuse apex. Dark green and shiny.
– Top axillary inflorescence,. Shortly stalked flowers in little groups of 2-5.
– Shaped drupe fruit, orange or purple with very rich in nutrients, especially vitamin C.
– 3 seeds in each fruit
Varieties of acerola
- Variety B-17: common variety. It has a high content of vitamin C and an acid or sub-acid flavor. It’s the kind of variety that is used to make juices. It is the most found in markets.
- Dwarf variety: dwarf cultivar, up to 60cm. high. Tolerant of cold temperatures to -6 ° C.
- Variety Sweet Florida: shrub that produces large fruit with thick skin, resembling an apple flavor.
- Variety Sweet Manoa: very productive upright shrub.

Fruits and branches of acerola
Adequate climate and place of cultivation
– It can be cultivated in tropical and subtropical countries.
– Acerola must be grown in full sun.
– Drought tolerant and adapted to periods of drought and low rainfall climates.
– Juvenile samples are not cold-hardy. If adults, they can stand up to -2. In winter they should be protected from the cold.
– The tree has a shallow root system. You can grow it near some other crops.
Acerola required soil

–Soil type: clay or limestone, well drained.
– Soil drainage: The poorly drained soil can lead to flooding and, consequently, to root suffocation.
– Soil reaction: soil pH must be between 6.5 and 7.5. Calcium deficiency has to be be avoided.
Acerola reproduction
Acerola can be reproduced by seed and multiplied by cuttings.
– Sexual reproduction by seed: seed germination may have very low capacity and it is not always feasible. Choose seeds from plants that have not been exposed to cross-pollination with other species of fruit. Clean and dry the seeds treated with fungicide. The germination rate is 50% or sometimes only 5%.
– Asexual reproduction by cuttings: Performed in adult trees of 3-4 years old. You must take a cutting 12 – 15mm. thick and 25cm. long. Put it in a propagator with hormones until roots appear. It is the most used propagation method.
Other cultivation tips
– This plant produces fruit after 1,5 – 2,5 years after planting.
– It fruits from 3 to 4 times a year or more.
– Acerola is a rainfed crop. It should only be watered to foster flowering and in moderate amounts. It does not want over-watering.
– Protect it from frost in greenhouses or cover cover the tree with plastic
Picking up acerolas
For home use, the fruits are picked when fully ripe. If you want to make marmalades or jams, they can be harvested slightly immature, when they are changing from yellow to red.
Acerola pests and diseases
- Root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.) They cause serious problems to roots because they form a sort of swelling in roots, called galls. This especially happens when they attack the young trees. It affects the productivity of fruits.
- Insects: aphids, whiteflies, etc.
- Acerola weevils (Anthonomus spp.): Some are serious agricultural pests that limit acerola production.
- Fungi (Cercospora spp.): Cercospora is the main fungal disease, especially in tropical crops. It is characterized by spots on the leaves. Apply a suitable fungicide.
![]() More information about acerola.
More information about acerola.