Contents
- 1 DRIED APRICOTS OR “OREJONES”
- 1.1 What are the dried apricots?
- 1.2 How to make homemade dried apricots
- 1.3 What is the difference between “orejones” and fresh apricots?
- 1.4 Advantages of dried apricots
- 1.5 Some additives can cause asthma attacks
- 1.6 Additives in the dried apricots: The best ones, dried at home
- 1.7 More information on apricots.
DRIED APRICOTS OR “OREJONES”
What are the dried apricots?
The dried fruit called “orejones” in Spanish are dried peaches or dried apricots.
These fruits are dehydrated by sun-drying technique to exploit their properties in food off-season periods.
 Dried apricots
Dried apricots
How to make homemade dried apricots
We can get homemade dried apricots placing them on a few cane beds in the sun on days without moisture.
When they are dry, they are stored in sealed and dry containers.
What is the difference between “orejones” and fresh apricots?
The drying process involves a loss of weight. Usually we usually get a fifth of the initial fruit weight. What actually occurred is a waste of water.
This loss creates a dried fruit that prevents organisms can thrive in it. In this way you can keep for a long time without rotting.
Advantages of dried apricots
The drying process involves the loss of water. For example, in the case of dried apricots while the fresh fruit has almost 90% water, the dry has less than 8%. Moreover, this process involves increasing number of other nutrients as shown in the table below.
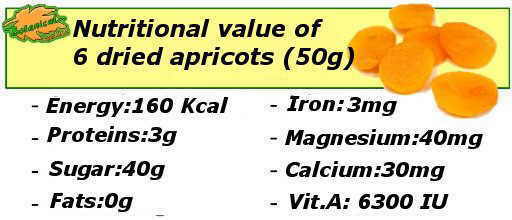
Summary sheet of the nutritional properties of dried apricots. 6 dried apricots equals 50 grams (1 serving).
Some additives can cause asthma attacks
It is best to dry the apricots at home than buying industrially dried apricots because in the drying process, components are added to the latter to improve its appearance.
For example, to avoid a blackened aspect it’s very common to add sulfur dioxide (E220). The additive can improve the appearance of them but it’s detrimental to health and it is often responsible for asthma attacks. Asthmatics should avoid eating dried apricots when they are not sure how they were dried.
A good way to know which dried apricots have been treated with sulfur is to notice the ones with a very vivid and bright color.
Additives in the dried apricots: The best ones, dried at home
It is better to dry the dried apricots at home than to buy industrially dried apricots, since, in the drying process, the latter contain added components to improve their appearance.
Thus, for example, in order to prevent them from blackening, the use of additives is very common. These preservatives that are added are sulfites.
 Dried apricots without sulfites. They do not have the orange color so attractive.
Dried apricots without sulfites. They do not have the orange color so attractive.
Sulfites are additives numbered in Europe from the number E220 to E228, such as sulfur dioxide (E220). These additives help to preserve the bright orange color of the dried apricots and to prevent their deterioration due to the attack of microorganisms.
These additives improve the appearance and conservation of the food. Sulfites have also occasionally been linked to adverse reactions such as vomiting, abdominal discomfort, headache and nausea.
It can be harmful to health and in sensitive people is usually responsible for asthma attacks in people suffering from this disease. Asthmatics will avoid eating dried apricots when they are not sure how they dried.
In addition, it has been observed that sulphite additives are related to migraine due to DAO deficit.
A good way to know that the apricots of the market have been treated with sulfur is to realize that they have a very bright and lively color. If they have a bright orange appearance it is recommended to avoid their consumption in asthmatics or sensitive people.
Related information: Nutritional value of dried apricots / Nutritional properties of dried apricots /Apricots in the kitchen








