Contents
- 1 MEDICINAL PROPERTIES OF HIBISCUS
- 1.1 REMEDIES WITH HIBISCUS
- 1.2 Hibiscus compresses are very suitable for skin care
- 1.3 Hibiscus for hypertension
- 1.4 How to make the natural treatment with hibiscus for hypertension?
- 1.5 Hibiscus for respiratory diseases
- 1.6 Hibiscus for digestive system diseases
- 1.7 Other traditional uses of hibiscus
- 1.8 EDIBLE AND INDUSTRIAL PROPERTIES OF HIBISCUS
- 1.9 Is hibiscus safe?
- 1.10 Other species of hibiscus
MEDICINAL PROPERTIES OF HIBISCUS
REMEDIES WITH HIBISCUS
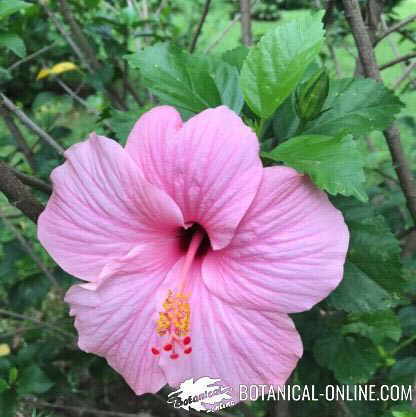

Pink hibiscus flower
Hibiscus compresses are very suitable for skin care
Common hibiscus, like all other plants in the mallow family, is rich in mucilage, some sugar component that confer it emollient properties, that is, it moisturize and protect the skin. For this reason it can be used to alleviate many skin conditions, such as wounds, cracks, sores, pimples, cuts, burns, sunburn, etc.
The most common way is to make a tea with a teaspoon of dried leaves and flowers per cup of water. With this infusion wet a compress and apply it on the affected area.
Hibiscus for hypertension
Hibiscus is an effective antihypertensive. Experts attribute these effects to the anthocyanin content of the plant. It treats of powerful antioxidants with capacity to diminish the capillary fragility and improve the circulation. In addition, these components also help to decrease the levels of bad cholesterol (LDL cholesterol), exerting a protective effect of cardiovascular health.
Besides, given its content in potassium, which provides a great potential to remove body fluids, it is also beneficial in the treatment of hypertension.

Photo of hibiscus candied with sugar, made with the flower of Jamaica or rose of Jamaica (Hibiscus sabdariffa). It is convenient to look for the dry flower, without sugar, because the consumption of sugar increases the cardiovascular risk.
Current scientific studies have shown how a species of hibiscus, called Jamaica flower or Jamaica rose (Hibiscus sabdariffa) has a mild antihypertensive effect, just as effective as some drugs used for hypertension such as lisinopril.
An extensive review of scientific studies (meta-analysis) of 2015 concluded that the infusion of this plant produced a significant decrease in blood pressure, therefore it has an interesting potential as a plant for the natural treatment of hypertension
How to make the natural treatment with hibiscus for hypertension?
- Infusion of hibiscus flower
- Use tincture of hibiscus that can be found in pharmacies or herbalists according to the conditions of the leaflet
- Extract of Hibiscus sabdariffa
- Hibiscus candied with sugar is not recommended, since sugar increases the risk cardiovascular)
- Consult the doctor
Hibiscus for respiratory diseases
To remove cough, hibiscus steam vapors can be considered especially useful. They are carried out adding a few drops of hibiscus extract in hot water.
Preparations of these plants are also used to combat other respiratory diseases such as influenza, bronchitis or colds.
Hibiscus for digestive system diseases
Infusions of these plants can be used to treat digestive problems that refer to anomalies of the mucous membranes, such as gastritis, indigestion or heartburn. (Infusion of a teaspoon of dried plant per cup of water. Take a couple of cups a day)
Other traditional uses of hibiscus
- Fever: Its citric acid content provides antifebrifugue properties. In order to reduce fever, make a tea with a teaspoon of dried petals per cup of water. Take a couple of cups a day.
- Hair loss: This same infusion is appropriate to strengthen the hair roots preventing alopecia or baldness. You can also use the fluid extract, that can be found in pharmacies or herbalists. (Use according to the patient’s leaflet)
- Cancer: Hibiscus is being investigated to inhibit the growth of cancer cells.
- Stimulating
EDIBLE AND INDUSTRIAL PROPERTIES OF HIBISCUS
- The young leaves and flowers of hibiscus are edible: Also dried or fresh flowers can be eaten. In some Asian countries they are served pickled for flavoring salads.
- Dyes: With its petals juices black dye is obtained. In China is abundantly used to dye the shoes.
- Fibers: From the branches and young stems are obtaine fibers which are employed to make paper, textiles or fabric.Is it safe hibiscus?
Is hibiscus safe?
These plants, in high doses, are abortive, so they not should be used by pregnant women because they can induce abortion.
Preparations of hibiscus are not suitable for infants.
Also, many of the preparations contain alcohol, so small children or people who are undergoing detoxification should avoid taking them. As there are more than 200 species of hibiscus, you need to know for sure that it is adequate and non-toxic species.
For the above contraindications and by the fact they are slightly hallucinogenic, many specialists prefer to replace all hibiscus with safer plants, such as mallow or marshmallow.
Other species of hibiscus
In addition to China rose or common hibiscus, the other important species of hibiscus are:
- Rose of Sharon (Hibiscus syriacus): With a smaller size, it does not exceed 3 meters. It has properties similar to the common hibiscus. The flowers are smaller fromo 8 to 10 cm and more open. It is very common to find them as gardens or parks plants.
- Roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa): From the African tropics. It is distinguished by its bright red chalices. It can reach 5 meters. The medicinal properties are similar to previous hibiscus. Like all of them, the flowers contain a lot of vitamin C so, in the Caribbean. it is used to prevent scurvy.
As the above species, its tender leaves are edible and can be cooked as if they were spinach. Sabdariffa hibiscus is grown in many parts of Africa, America and tropical Asia. In these places it is taken as a tea in meetings with friends or acquaintances, fulfilling a social function. In addition, because of its refreshing properties, it is suitable in these hot places.
- Okra, okro, ladies’ fingers or gumbo (Hibiscus esculentus = okra) Another species of African hibiscus, though cultivated in the Caribbean, South America, South America and India. Unripe fruits are widely used for its richness in mucilage which gives a pasty consistency to stews with it, such as gumbo, a very traditional dish in Lousinia. As medicinal it is used for treating sexually transmitted diseases, especially syphilis and gonorrhea, as a result of its disinfectant properties.
- Manihot, hibiscus manihot, sunset muskmallow (Hibiscus manihot) It comes from the mountainous regions of Southeast Asia, reaching great heights on the rocky slopes of the mountains of Nepal. For external use.a paste is prepare with crushed leaves.The inhabitants of these areas use it to treat tumors and heal dislocations and stretches.
- Cotton rosemallow, Confederate rose (Hibiscus mutabilis) comes from China. It is a shrub about 3, 5 m high, with very characteristic leaves and young shoots, since they are covered with dense hairs reminiscent of cotton. It reaches about 3.5 meters high and produces usually solitary flowers about 10 cm in diameter by the fall. It is used to treat shocks.
- Swamp rosemallow, eastern rosemallow (Hibiscus palustris) is a perennial shrub that reaches a couple of meters high, growing in brackish or marshy places in Europe, Asia and North America. It has been used externally for the treatment of tumors.
- Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus) is an annual or biennial hibiscus, widely cultivated in southern India for the production of a type of fiber like jute called kenaf.
This fiber is used for the production of bags and ropes. Oil is extracted from the stems. It is rich in omega 3. As a medicinal plant, it is used for healing wounds, to reduce fever, as an aphrodisiac, as stomachich and appetizer.
- Blue mahoe: (Hibiscus elatus= Talipatiri elatum) Natural from Caribbean, it reaches 25 m. high. The wood is highly appreciated for the construction of furniture and musical instruments. Whole leaves a very large.
Red or yellow flowers up to 20 cm in diameter. It has been planted in parks in warm weather for the beauty of its flowers and the considerable size of its leaves, that provide great shade and protection from the heat of summer.
As a medicinal plant, it has antipyretic, emollient, antidisenteric and laxative properties.
![]() More information on hibiscus.
More information on hibiscus.