Contents
HOW TO GROW DURIAN
What is durian like?
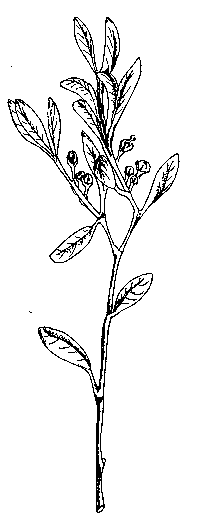
Durian is a fruit tree, native to the rainforests of Indonesia. Very long-lived tree, it can reach 150 years of age and even more. Height between 20 and 50m. Trunk diameter of 120cm. and up to 200cm. Its trunk cylindrical, woody, often cracked, with a rough surface. Dense irregular crown.
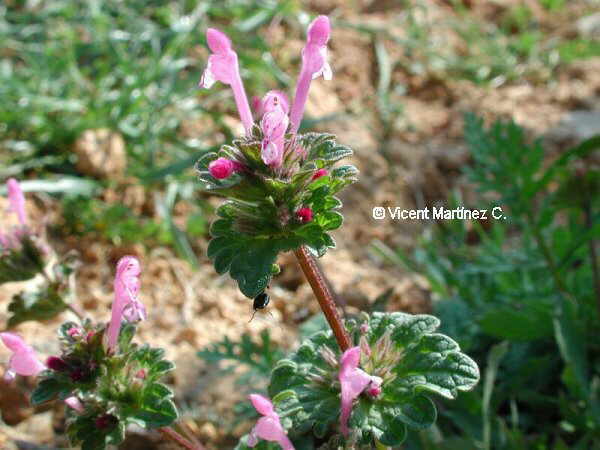
Durian leaves are large, 8- 20cm. long; 2.5-7.5 cm. wide. They are elliptical or oblong, limbo is bright green and golden on the underside.
Durian flowers grow in clusters of 1-30 individual flowers, which rise in the branches or the main trunk of the tree. Each flower has 5 sepals and 5 petals, yellow, white or red. The petal color determines the color of the fruit pulp. Thus, for example, trees with red flowers produce red flesh durians.
They are hermaphrodite, having seven stamens and a pistil. However, the two parts appear in different times, so that there is no self-pollination.
They are very fragrant and are pollinated by insects.
Durian fruits and seeds

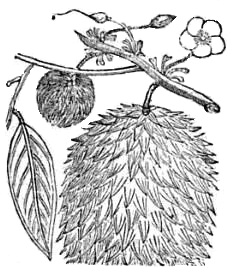
Durian fruit is oblong, hard-shelled, thick, green and prickly. The interior is made up of five compartments, which contain from 1 to 7 seeds, coated with a meaty aryl.
The aryl is what is commonly known as ” flesh “, and consumed in the diet. Actually, a fleshy integument protecting seeds and botanically formed from seed funiculus.
Durian fruit weighs between 2 and 5kg., Sometimes up to 8.
Durian seeds are reddish brown and are 2 to 6 cm long. They are dispersed by frugivorous animals (animals that eat fruit) as primates.
Currently, these animal species, including the orangutan of Borneo, are endangered, which will influence on the natural distribution of durian in the long term.
Suitable climate for durian
- Tree of Indonesian rain forest, adapted to high amounts of precipitation (Annual Rainfall higher than 2000mm)
- It requires moisture to grow. Ideal planting place: near rivers, ponds or places near water.
- Soil deep, gritty and frank. Optimal alluvial soils
- PH: 5 – 6.5
 PROPAGATION OF DURIAN
PROPAGATION OF DURIAN

Seed propagation
- This type of reproduction produces robust trees up to 50 m. high when conditions are optimal.
- This tree does not bear fruit until 7 years of age, although its fruits are of very good quality, size and taste. The trees are usually grafted.
- The seeds should be purchased from fresh fruit, because they lose the ability to germinate in a few days. Do not let them dry or be exposed to the sun.
- Prepare the seed in a bag of 8 liters. They will germinate quickly.
Graft propagation
- Trees made by shield graft technique begin to bear fruit at 4 years. Full production at 12.
- Patch and Forked methods can be used.
 Fertilization of durian
Fertilization of durian
It is recommended to fertilize it with green fertilizer, manure, or compost.
Flowering and fruiting of durian

- To stimulate flowering, it is required a period of 3-4 weeks of dry weather.
- Durian flowers open at noon and close at midnight (anthesis), so that bats play an important role in this plant pollination.
- Durian matures between 85 and 150 days after pollination.
- The fruits, which arise from the branches or directly from the trunk of the tree, are abundant. In Indonesia it is customary that people camp out near the fields to harvest the fruits durians for 6-8 weeks, . These fruits are very perishable. They mature after 4 days from falling, and soon after, they begin to perish quickly.
 Collecting durians
Collecting durians
- A young durian tree can produce 10-40 fruits fruiting the first year, 100 in the sixth year and 200 in the tenth year of production, provided that the conditions are favorable.
- Due to the weight, hardness and thorny rind of the fruit, it is dangerous to go near a tree of durians when they drop . There have been some serious accidents in areas of Indonesia by the accidental fall of durians over people. Networks are usually placed to capture the fruits, or they are attached to the tree to avoid them falling when ripe.
 Pests and diseases of durian
Pests and diseases of durian
- Scale insects: Durian may be liable to be attacked by the white mealybug (Pseudococcus lilacinus) and giant mealybug (Drosicha townsendi).
- One of the few diseases that attacks the durian is the fungus Phytophthora palmivora, during the first years of the tree. Infection is detected as a sludge on the plant.
![]() More information on durian.
More information on durian.