Contents
- 1 (Litchi chinensis= Nephelium litchi)
- 1.1 HOW TO GROW AND TAKE CARE OF LYCHEE
- 1.2 What is lychee?
- 1.3 Weather requirements for lychee
- 1.4 Lychee needed soil
- 1.5 Lychee propagation
- 1.6 ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION BY CUTTING:
- 1.7 Lychee pruning
- 1.8 Lychee harvest
- 1.9 Lychee Fertilization
- 1.10 Plagues and diseases of lychee
- 1.11 Where are lychees produced?
(Litchi chinensis= Nephelium litchi)
HOW TO GROW AND TAKE CARE OF LYCHEE
 What is lychee?
What is lychee?
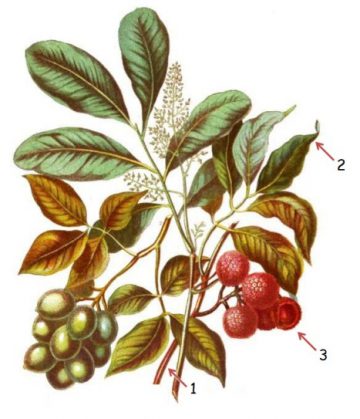
Lychee (Litchi chinensis) is a fruit tree of subtropical climate, always green and of height not superior to 10m. It belongs to the Sapindaceae family, the same family to which longan, guaraná or rambutan belongs.
– Trunk erect, with brown and branched bark, with rounded crown.
– Leaves petiolated, alternate and compound, elliptic-oblong, smooth, bright and dark green above and greyish green on the reverse.
– Inflorescence in the form of floral clusters, axillary or located in the terminal part of the branches.
– Fleshy fruit, popularly known as lychee, heart shaped, thin pericarp, hard, brittle and with numerous conical protrusions, pink or red. The edible part of the fruit is a pulpy, translucent white pulp.
– Seeds, dark brown and shiny.
Weather requirements for lychee
Photograph of litchi in a terrine, as it is usually presented on the table.
– Tropical and subtropical climates.
– The optimum conditions are dry and hot summers and cold winters (without frost).
– It does not tolerate frost.
– It can grow at different altitudes, although it prefers low altitudes.
– Annual precipitation 1,200 – 1,600mm.
– Relative humidity around 75%. Trees located in humid climates are more productive, such as those near areas to rivers or in the coast.
– Protect from wind.
 Lychee needed soil
Lychee needed soil
– It tolerates all types of soils.
– Soils sandy, silty (sandy-loamy) and even clayey.
– The recommended pH is between 5.5 and 6.5.
 Lychee propagation
Lychee propagation
SEXUAL OR SEED PROPAGATION:

– The seed of lychee germinates a few days (4-5 days) after the fruit harvest. It is for this reason that the tree has taken several centuries to extend beyond its geographical area (China).
The earliest records of lychee cultivation in other countries date back to 1854, in Australia; And in the year 1870 on the islands of Madagascar and Mauritius. It was not until 1883 that lyche arrived in America, in Florida.
– The fruits with aborted seeds (of very small size and with seeds little developed) are sterile.
– Grow in a greenhouse for at least the first winter. Protect from frost. (More information)
– Transplant with stake (50cm depth) in definitive soil in late spring or early summer. Maintain spacing of 5-6 meters between each tree so that each plant can have all the nutrients in the soil. (More information)
– Some authors mention that this type of reproduction produces trees that are not long lived and also late in production, since they begin to fructify at 8 years.
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION OR BY AIR LAYERING
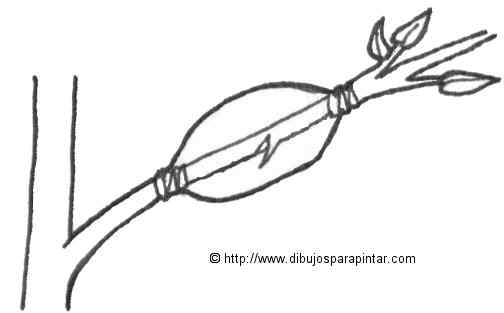
A drawing of how to realize an air layering (More information)
– It is the most widespread medium for the reproduction of lychee. It is done in spring.
– It consists in choosing an adult tree of lychee, with abundant ramifications.
– Select a branch of and old specimen (young shoots do not root), with a diameter of 2cm. or slightly less, and at least 60cm long.
– Cut the leaves and shoots of the selected branch in the first 15 or 30 cm leaving the shoots and leaves at the end.
– With a razor knife or a clean and sharp knife, a ring of bark less than 1 cm wide is removed in the middle of the clean part of the branch. On this cut, hormones are applied to stimulate root growth.
– Transplant in definitive terrain in the rainy season.
– Maintain minimum separation between trees of 15m. or more.
– The tree produces fruit between the first 2-5 years, and will be more productive from the 20 years.
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION BY CUTTING:
– Generally this method has proved ineffective in lychee.
Lychee pruning
– Lyche needs pruning to develop a strong structure and to increase fruit production.
– It is carried out after harvesting during three to four years after planting. It consists of heading the young shoots at 80cm. from the soil to favor the development of main branches. When we have already cut the young shoots, we proceed to prune the shoots of the secondary branches. See animation.
– From the fifth year on, we will only prune branches that grow inward, twigs too close or double, branches dry or diseased.
 Lychee harvest
Lychee harvest
Harvesting of fruits is done in late summer, when the conical protuberances appear in the pericarp (“skin”).
 Lychee Fertilization
Lychee Fertilization
– It is recommended to pad the ground in spring, with organic matter (manure, compost or bark), especially during the first three years of the tree.
– Lychee requires soils rich in organic matter to grow and develop its fruits, especially the first years of cultivation.
 Plagues and diseases of lychee
Plagues and diseases of lychee
- Root rot: in fields where other types of fruit trees have been harvested previously or by excessive irrigation.
- Postharvest rot: it occurs in fruits that have not been treated with fungicides mainly, which are susceptible to fungal infections.
- Mites: especially it is attacked by the spider of the lychee or lychee erinose mite (Aceria litchi) and the litchi rust mite (Eriophyes litchi). The spider of the lychee causes what is known as curly leaf of lychee, being one of the main pests that affects this crop. It is a pest that damages leaves and flowers, causing blisters and wrinkles in the leaf blade and deforming them. It can kill young specimens.
- Sting bugs: the main insects are Banasa lenticularis, Lyramorpha rosea and Tessaratoma spp., Especially lychee giant stink bug (Tessaratoma papillosa). Species with red and bright spots, it feeds on the sap of the leaves and young shoots producing the death of the affected twigs and leaves.
- Caterpillars: The lychee can suffer some type of pest produced by caterpillars. The Light Brown Apple Moth (Egiphyas postvitana), damages the leaves of the plant. The caterpillars or borer caterpillars, such as the Bark Eating Caterpillar (Indarbela quadrinotata) damage the trunk of the tree in its larval state, directly influencing the lower growth and development of the tree. Preventive treatment.
- Coccides (Coccidae): Coccidian Coccus viridis, a type of insect, attacks the leaves, fruits or shoots of the plant. The leaves become sticky and charred in appearance, which attracts ants and in turn contributes to the dispersal of the pest.
Before being banned, it was treated with chlordane. Currently this pesticide is prohibited because it is toxic to man and accumulates in the human body. It is recommended to use other pesticides, remove the affected leaves and fight the ants, which carry the affected leaves.
- Fruit flies: They deposit the larvae inside the fruit, and sometimes cause fermentation of the fruit, which causes cracking and rotting.
- Birds and bats: they are consumers of the fruits.
Where are lychees produced?
| Main countries producing lychees (FAO 2002) | ||
| Country | Area of cultivation (ha) | Production (in tonnes) |
| China | 580.000 | 1.260.000 |
| India | 56.200 | 428.900 |
| Thailand | 110.000 | 190.000 |
| Taiwan | 11.580 | 108.668 |
| Vietnam | 35.352 | 50.000 |
| Nepal | 1.792 | 13.875 |
| Bangladesh | 11.875 | 12.876 |
| Mexico | 2.402 | 9.728 |
| Australia | 1.500 | 3.500 |
| One of the most important lychee growers was Reverend W.M. Brewster, who selected the best lychee cultivars in the years 1903 and 1906. Currently, the most widespread cultivar of lychee in the United States. And Mexico bears his name. |
![]() More information on lychee.
More information on lychee.

 Lychee Fertilization
Lychee Fertilization