Contents
- 1 History of traditional remedies with plants
- 1.1 The oral tradition
- 1.2 Finding a new medicinal plant was a risky business
- 1.3 Chance took a great importance on finding new medicinal plants
- 1.4 When did the first written texts on medicinal plants appear?
- 1.5 Examples of medicinal plants usage in the past
- 1.6 What is the first scientific medicinal plant book?
- 1.7 Medicinal plants in the Middle Ages
- 1.8 The contribution of the New World
- 1.9 A universal legacy that that must be preserved
History of traditional remedies with plants
The oral tradition
Nobody knows exactly where medicinal plants were used for the first time. Surely the search of some remedy was something that occurred simultaneously in all the cultures, fruit of the desire of the man to heal, for magical-religious reasons or because of some preparation that provided a great temporary happiness.
Most times the discoveries were simply results of the search of new types of food.
Finding a new medicinal plant was a risky business
The ancestors had to verify if the new species were foods, something that took them to discover in there own body that many of them were evidently foods; other poisonous, and others produced somewhat different effects: they increased the sweat, they made them defecate with greater facility, eliminated the joint pain that until the moment had produced them much discomfort, etc., etc.
Chance took a great importance on finding new medicinal plants
Other time, it was simply the result of chance what delivered new samples.
Thus, for example, it is told that a Spanish soldier discovered by accident that the quinine, main component of cinchona, could cure the intermittent fevers: apparently he drank of a pool where a branch of this tree had fallen and that the fever was gone when he woke up.
Whatever the case might be, Man began to understand the medicinal properties of plants.

Some medicinal plants illustrations
When did the first written texts on medicinal plants appear?
Knowledge on the medicinal plants, before the birth of writing, were transmitted orally.
It is known that the first written text on the use of medicinal plants is about 4000 years old and appears in a clay small board in the Sumerian culture, an antique groups of people who lived at the south of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers, which would be equivalent to the current Iraq territory.
Examples of medicinal plants usage in the past
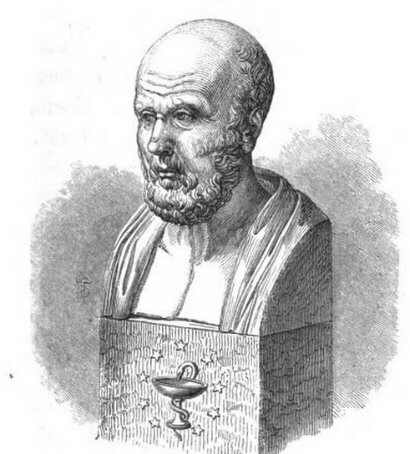

19th century drawing of Hippocrates, ( from Ancient Greece, 460 BC – 370 BC), who is considered the Father of Western Medicine
- The Egyptians used the principles of the medicinal plants in a systematic and controlled way.More than 700 formulas with plants are known, and the most interesting printed document is the Papyrus of Ebers, from 1700 A.C., but, for sure there was a previous use of these plants in Asia, mainly in China, where it is assumed that they were already used in 5000 A.C.
- The Greek and the Romans pick up the tradition of Mesopotamia and Egypt. They make use of the plants to cure the diseases and to maintain a good state of health.Thus, for example, the Greek physicist Hippocrates (Island of Cos in Greece – 460-c. 377 a.C.), considered the Father of Western Medicine, grants extreme importance to the preventive medicine and, within this, the plants play a very important role, until the point that he is considered the author of the following aphorism: “Let your food be your medicine and your medicine be your food”.
- In China, A good example is the book Pen Tsao that gathers the study of more than 300 plants.
- In India the use of medicinal plants, known like Ayurveda, has left written references from 800 A.C., where they describe 800 species.
The Ayurveda, a way of life that implies medicine, religion, philosophy or science generally proposes healthy life habits to secure a total health. The medicinal plants would constitute an important resource, along with the diet or the exercises.
The ayurvedic medicine shares its methods with those of “the official” medicine; it is the way to face the diseases of the poorest classes of this country and it is extending in other western countries like one of the main alternative medicines.
What is the first scientific medicinal plant book?

19th century drawing of Dioscorides
The first writing of scientific nature at the classic time is Medical Matter, written by Dioscorides (40-90 d.C.). It is a work in five volumes. This Greek, natural of Anazarbus, Cilicia (a country that would be equivalent to present Turkey) worked with the Romans as a botanist, which allowed him to travel much.
During his trips he studied the properties of 1000 plants and many chemical principles and his work served as reference until XV century. His work has been revised and translated many times.
The most important revision in Spanish is “Plantas medicinales, El Dioscórides renovado” of Catalan pharmacist Pio Font Quer. In his work the author reviews 682 species, mentioning the opinions of Dioscorides and the revisions of Pietro Andrea Mattioli and Andrés de Laguna.
Medicinal plants in the Middle Ages
During the Middle Ages, the study of the medicinal plants was in the hands of the monks who in their monasteries planted and experimented on the species described in classic texts.
The contribution of the New World
Aside from this European tradition, the importance of the culture and use of medicinal plants in the New World has to be mentioned.
When European colonizers arrived in America they were fascinated by the knowledge that the natives had on the medicinal use of the plants.
These knowledge was in the hands of shamans who were those who had the power to use magic and medicinal plants to cure the diseases. There were many later expeditions of botanists and herbalists who looked for a greater knowledge of the curative properties of the plants.
A universal legacy that that must be preserved
The knowledge of the medicinal plants extends to any part of the world where man has traditionally needed these plants to cure his diseases.
Thus, through a mixture of magic and religion, of necessity and chance, of test and error, different cultures have created a knowledge of vegetal remedies that has formed the base of the modern medicine.
A patrimony that cannot be attributed to any culture in particular but to the whole human race and which we all should know and preserve.
![]() More information on medicinal plants.
More information on medicinal plants.