Contents
Box elder care
Description of box elder

Perennial tree belonging to the Araceae family up to 30 m.
Light grayish trunk when the plant is young and darker as it gets older, with protuberances.
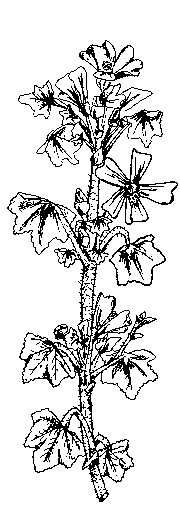
Opposite compound leaves up to 15 cm., formed by leaflets, in number from 5 to 7. Pointed leaflets with serrated edges.
Dioecious tree with male and female specimens. The fruits are samaras, as in the rest of the “Acer” genus, which have a length of about 5 cm.
Flowers in clusters without petals. It blooms in April or May.
Box elder cultivation (Varieties)
Native to the eastern United States and Canada. It reaches as far south as Mexico and Guatemala, although it appears very frequently planted in gardens and parks in many parts of the world as an ornamental tree. The variety “Variegatum” is the most widely used. Other known varieties are “Baron” and “Flamenco“.
It is a fast-growing tree with a moderately short life, reaching about 75 years.
Box elder (Uses, land, irrigation)
In the wild, it coexists with other riverside trees, such as poplars or willows. It prefers to grow in soils that retain moisture for a long time (on the edge of streams, lakes and wet lands) since the root system is formed by broad and shallow roots. It does not support very deep terrain. The most appropriate would be the sandy ones. During growth it needs to have constant humidity, although, once it has grown, it can withstand drought quite easily. Likewise, this tree is adapted to growing in lands that have suffered flooding for a while.
On the other hand, its capacity for adaptation is so great that it can live perfectly in urban areas with high levels of pollution, with soils rich in debris or organic remains and low humidity. This characteristic is used to plant them in cities. It can even reproduce itself in this hostile environment, through the dispersion of its seeds, carried out by the wind, without the need for human intervention. In addition to being used as a garden, park or city tree, it is a species that is also cultivated as bonsai.
Industrially, its wood is light, not very resistant and very easily to rot. It is used mainly as fuel. From a medicinal point of view, the application of some of its components for the treatment of cancer is being investigated. In terms of food, the American Indians have used its sap to make syrups and sugar.
Box elder (Exposure)
Although the preferred location is sunny, it can be partially shaded. This tree even tolerates shade.
Box elder (Cultivation and diseases)
It can be reproduced through seeds (these are left hanging on the tree for most of the winter. They represent one of the few sources of food for animals, especially birds). Another way of reproduction is through cuttings.
This tree has a great ability to regrowth, when the main tree has been cut or has been felled by some accident.
It should be pruned in the middle of summer.
It is a tree that has a great tendency to suffer internal rot, caused by fungi of the genus Phytophthora. Therefore, when it is planted in cities or gardens, it requires a control that prevents it from breaking. Improved drainage is necessary to avoid this disease. It is advisable to get rid of the affected plants. Gall mites, in the form of whitish or reddish crusts, also attack its leaves and it is necessary to get rid of the branches that are affected. It is also frequently attacked by other insects.
![]() More information on plant cultivation
More information on plant cultivation