Contents
PLANT POLEN
What is pollen like?

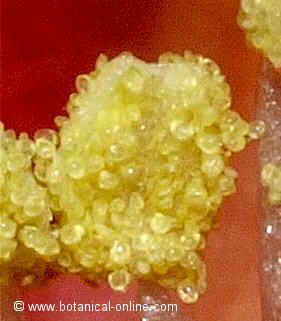
Pollen is a kind of fine powder produced by flowers. This powder is formed by pollen grains.
Each pollen grain contains within it the gamete or male reproductive cell of the flowers, destined to fertilize the ovule, that is the gamete or feminine reproductive cells of the flowers.
Pollen develops at the end of the anthers of the stamens in containers called pollen sacs.
Each pollen grain is protected in its exterior by a cover called exine, formed by very resistant materials that are able to withstand the external aggressions being able to remain unchanged for thousands of years.
This has allowed the development of a science called Palinology that, in addition to studying the composition of pollens and other aspects of the same, allows to find out which plants belong to the pollens buried in the fossil soils.
In this way, you can know what kind of plants existed in a given period in a certain place.
What is pollination?
In order for germination to take place, pollination of pollen must be produced beforehand. Pollination is the transfer of the pollen from the anthers of the stamens of male flowers or male part of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or of a different flower
Once on the stigma, the pollen grain matures, producing a pollen tube that penetrates the style and reaches the ovary where it fecundates the eggs. (See animation about pollination. Click on the image to see what happens to the flower once pollinated.)
Types of pollination
- Self-pollination: When pollination is carried out within a single flower (hermaphrodite flowers) is known as self-pollination or autogamy. It is the simplest way of pollination, although it is the one that has less genetic quality and therefore more susceptible to possible degenerations.
- Cross-pollination: When pollination is carried out between flowers belonging to flowers other than the flower belonging to the pollen is called cross-pollination. This can be carried out between different flowers of the same plant, in which case it is known as geitonogamy. When it is produced among flowers of the same species in different plants we call it xenogamy.
Cross-pollination is more complex than self-pollination although it implies a greater contribution of healthy genetic material. For example, seeds produced between plants that come from cross-pollination are more resistant to inclemencies and pests.
To avoid self-pollinating plants have developed a series of adaptations, such as producing totally male or totally female, such as willow or holly. These plants are called dioecious. Other times the plants develop the male flowers in some branches and the female flowers in others, as it happens in the oak.
At other times, when flowers are hermaphrodite, to avoid self-pollination, they produce chemical components that prevent the pollen grain from producing the pollen tube that should reach the ovary; They can also develop very long stigmas that put the pollen of a same flower far from the reach of the same, as it happens in the hibiscus. Even more effective is the fact that in the same flower the male and female sexual apparatus mature at different times.
What are pollinators?
Animation of a bee collecting nectar from a flower. Click on the drawing to see the animation. |
Pollinators are agents capable of transporting the pollen. The main pollinator is the wind. Plants that are pollinated by the wind are called anemophiles.
Among these we have the gymnosperms and especially the conifers (pines, firs, etc.) In all of them there is a cross-pollination.
Large masses of pollen are swept by wind and fall on other trees, many of them located at enormous distances. (Anemophilous pollination)
Other times pollination is done by the animals (zoofily) The pollen sticks to the hairs of these when they visit a flower and is unconsciously deposited in the stigmas of another flower.
The main pollinators of the animal world are insects (moths, male mosquitoes, adult beetles, wasps, male horseflies, etc.) some pollinating mammals (bats) and some birds, such as hummingbirds.
How do bees pollinate?
Bees have small hairs that collect pollen. They pick it up in a special bag they have on the hind legs called a corbicula or pollen basket ”
Within the insects, bees stand out as the main pollinators. Bees use pollen and nectar from the flowers for feeding. Pollen gets the proteins and nectar, the calories. Also larvae are fed by pollen.

The body of the bees is adapted to collect the pollen. The bees take it from the flowers and mix it with their saliva.
Subsequently, they hook it in their legs forming a kind of bag (corbicula o pollen bag). Then, they take it to the hive and place it in a honeycomb cell that they then cover with wax. In this way it is stored as a reserve food. That is why pollen is also known as “honey bread”.
In addition, since the body of the bees is hairy, another pollen involuntarily engages the hairs when visiting the stamens of a flower. When the flowers are changed, some of the pollen from the previous flower is released and stays on top of the stigma of the new flower.
Crucial importance of bees in maintaining species
Maintaining the richness and variety of pollinators is paramount so that plants can continue reproducing with complete normality. Being the most important pollinators, it is especially necessary that bees continue to enjoy perfect health and their existence is not threatened.
Bees have become the main pollinator insects of cross-pollination. Hence the importance of these insects in the continuity of plant life.
The death of large numbers of bees in recent years, especially by bee predators, such as the European hornet (Vespa cabro), and the use of insecticides, poses a danger to the continuity of numerous plant species, including most of vegetable origin.
According to recent studies conducted in the United States, during the winter of 2014-2015 there was a loss of bee colonies of almost 42%, which is three times more than 15%, a number that, according to beekeepers, would be Within the usual values. In Europe, the country with the largest loss of bees is the United Kingdom.
It is of vital importance the conservation of these insects through studies on the enemies of the bee that allow to solve the problems that their decrease.
Photo of bee sipping a rosemary flower.
Note the whitish pollen grains attached to the hairs on the back and the pollen bag of the hind paw
Pollen as a supplement to the human diet
The pollen collected by the bees is collected by the men and, after being subjected to a dehydration process to avoid spoiling, it is packaged and put on sale for human consumption.
Due to its content in vitamins, minerals and amino acids, it is a product that has many beneficial properties for our organism.
![]() More information on pollen, honey and other bee products.
More information on pollen, honey and other bee products.









