Contents
What is a marshmallow?
Characteristics of marshmallow (Althaea officinalis)
Common English Name: Marshmallow, Marsh mallow Canamera grass
Common name in other languages:

Photo of marshmallow leaves and flowers
Scientific name: Althaea officinalis L.
Family: Malvaceae
Habitat: It grows in most of Europe, in humid places hence its English name of Marsh mallow (Its name meaning a type of mallow that lives in marshes). It also appears in brackish seaside land in ditches and wet meadows.
Particularly abundant in the Caspian and Black Sea and the western Asian steppes where it looks like it comes from. It can also be found in North Africa and in the northeastern United States where it has been adapted after being imported as a garden plant.
Description of marshmallow
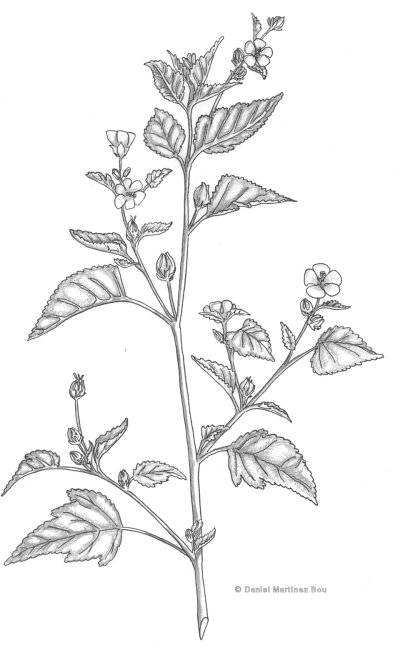

Botanical illustration of marshmallow
Perennial plant of the mallow family up to 2 m tall.
Simple or usually multiple, round and strong, annually renewable woody base stems which arise from a fibrous root, elongated cone-shaped, with white flesh inside and the outside yellowish, penetrating deep into the earth.
Lower leaves cordate, textured velvet, up to 7.5 cm long, short-stalked irregularly lobed; upper triangular.
Flowers showy pink or white, often white-pink, clustered in groups of up to 3 racemes, shortly stalked.
Fruit with a single seed.
Components of marshmallow
- Acids: ascorbic acid, butyric acid, ferulic, malvalic, chlorogenic (Ground), p-coumaric acid, syringic, caffeic, salicylic acid (leaves)
- Mucilage: (root and leaves)
- Paraffin (plant)
- Carbohydrates (root)
- Alkaloids: betaine (root)
- Amino acids: asparagine altheine = (root)
- Starch (root)
- Pectin (root)
- Fiber (root)
- Tannins (root)
- Lecithin (root)
- Vitamins: B vitamins: riboflavin, niacin, thiamin (root); beta-carotene (root) and vitamin C (root)
- Minerals: aluminium, calcium, cobalt, chromium, iron, magnesium, silicon, sodium (root)
- Alcohols: faradiol, taraxasterol, arnidiol, beta-sitosterol (Flower)
TRADITIONAL USE OF MARSHMALLOW
Properties of marshmallow as a medicinal plant
Marshmallow is one of the most important emollient plants. This property is characterized by softening, protecting and moisturizing the mucous membranes of the skin.
This effect can be explained by the ability of its components to prevent the evaporation of water so that a kind of protective layer or film is formed on the skin or mucous membranes, which keeps it more hydrated.
Paraffin, mucilage and starch would be the main components that provide this property.
Demulcent properties of marshmallow (mucilage)
 Marshmallow flower
Marshmallow flowerMarshmallow is also one of the best demulcents, which are the substances that are capable of relieving the irritation of the mucous membranes. The demulcent properties are granted for its richness in mucilage, pectin and sucrose.
These sugary components, especially the mucilage, in contact with water, form a kind of protective paste, similar to a gelatin that cures or prevents inflammation and relieves pain, while producing a medium where microorganisms can not thrive.
These properties have been widely recognized more than 2000 years ago due to the wide use of this plant both as a medicinal plant and for its food properties.
![]() More information on marshmallow.
More information on marshmallow.