COMPARISON OF NUTRITIONAL PROPERTIES OF DRIED FAVA BEANS AND TENDER FAVA BEANS
Nutritional differences between tender and dried broad beans
Looking at the composition tables, one could say that dried beans seem more nutritious than broad beans, but it is not so, because, when dried beans are cooked and hydrated, they end up having a very similar nutritional composition to the tender ones.
The explanation is simple, as food wins water, it increases in volume (gain weight) but its nutritional density is reduced, then 100g brings more water and less carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, etc.
Green broad beans and dried broad beans, once cooked, have a similar nutritional composition, but not identical.
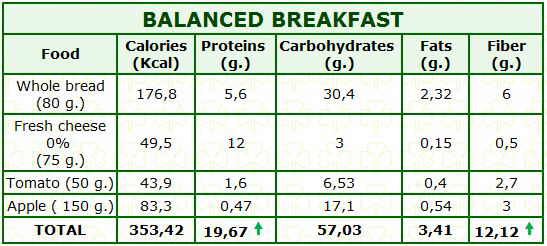
If you look at the protein content, as well as tender broad beans provide 5.6 g of protein per 100g, when cooked, dry fava beans reduce its content from 26 to 8 g protein per 100g.
Something similar happens when calories are valued.
Conclusion: What is the difference between eating tender and dry beans?
The nutritional value of dried beans is similar to fresh beans in terms of macronutrients and minerals. You could only see an important difference between the dry and tender beans in their vitamin content.
Tender fava beans are richer in vitamins than dry fava beans. This is because during the long soaking and cooking, water soluble vitamins such as thiamin, niacin and riboflavin are dissolved and lost in the cooking water.
During this process of preparation and cooking, significant potassium loss also occurs. Beans conservation also reduces their vitamin content.

Photo of tender beans
Which fava beans are better, dry or tender?
Fava beans are very nutritious both dry and tender, because they provide good amounts of vegetable protein, fiber, vitamins and minerals such as iron and magnesium.
We can also say that tender broad beans are richer in vitamins, chlorophyll and flavonoids than dry, so they will be slightly more diuretic and antioxidant.
Legumes increase the digestibility of its protein and vitamin content when they germinate.
* Learn more about the benefits of beans in the listing below.
The best way to consume beans
How to eliminate anti-nutrients in grains and legumes?
The best way to eat beans is germinating them because germination improves the digestibility of the seed and increases its nutritional properties. Germination increases the vitamin content of fava beans and decreases their anti-nutrient content. That is, substances present in the seeds, which inhibit or prevent absorption of nutrients, reducing their nutritional value.
In the tables of food composition you can see only the total values of macro and micro nutrients (proteins, carbohydrates, iron, calcium, vitamins,….), as shown above tables with beans. But nutritional tables do not take into account other substances on food modifying their nutrient digestibility.
Like many legumes, fava beans have components known as antinutrients, which inhibit or prevent assimilation of nutrients. These antinutrients decrease the digestibility of proteins and carbohydrates (Among them, we have substances like saponins, protease inhibitor, amylase inhibitor, phytates, etc).

Photo of cooked dry beans
Advantages of germinating fava beans and other legumes
Cooking them in salted water content reduces anti-nutrients and makes them more digestible. One way to eliminate these anti-nutrients is soaking beans before cooking previously, and give them a long cooking.
If we boil fava beans too quickly, the high content of these substances will cause we can not assimilate much of its components and fava beans become very indigestible. Like other legumes, when not properly cooked, they produce much flatulence and swollen belly.
In germinated beans, antinutrient content is reduced and the content of vitamins and other substances is increased, such as amino acid levodopa (L-DOPA), precursor of the neurotransmitter dopamine and very interesting in diseases such as Parkinson’s. This procedure makes the components of seeds and similar food more bioavailable, thus making them more nutritious.
![]() More information on fava beans.
More information on fava beans.