Contents
What is a goldenrod?
Characteristics of goldenrod (Solidago virgaurea)

Common English name: Common Golden-rod, European Goldenrod, Goldenrod, woundwort
Common name in other languages:
Scientific name: Solidago virgaurea L (=Solidago virga aurea L.)
* See: Goldenrod in other languages
Family: Asteraceae
Habitat: Where to find goldenrod?
In scrubs, European and Mediterranean high mountain forests, meadows. It can be found at altitudes between 300 and up to 2,800m.
Distribution: Widespread in Europe, Eurasia and North America.
Botanical description of goldenrod
Perennial plant, rhizomatous, 20-100 cm tall.
Erect stems, pubescent, simple or branched only in the inflorescence.
Leaves alternate, stalked at base, lanceolate or ovate-lanceolate. Fewer upper leaves, sessile.
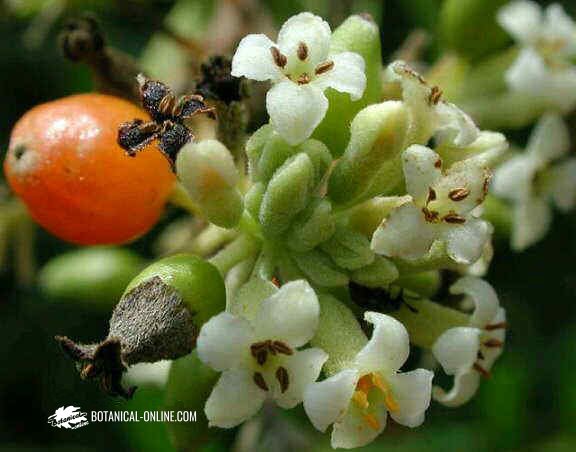
Flowers are gathered in chapters, golden yellow. The flower heads are a type of characteristic inflorescence of the Asteraceae or Compositae plants that are composed of tiny tubular flowers and marginal ray florets.
The fruit is an achene called cipsela, provided with pappus.
Collection and preservation of goldenrod
Goldenrod flowers from July to October. Its seeds ripen from August to October.
This plant must be collected during flowering, left to dry in the shade in a dry, airy place. Then it must be placed in airtight glass jars and store in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
The flowering tops and leaves are used for tea, syrups and preparations for topical use (compresses, poultices, lotions,…).
Composition of goldenrod
- Flavonoids (0.21.5%): hyperoside, rutin, astragaloside, isoquercitrin, leicarposide, quercetin, rutin,…
- Condensed catechic tannins or proanthocyanidins
- Saponosides: triterpenoid saponins (maximum in leaves in autumn)
- Coumarins
- Acids: Caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid, quinic acid
- Essential oil (0.10.5%)
- Mucilages (leaves), inulin (roots)
Uses of goldenrod
This plant of the Asteraceae family is used as:
- Colouring: Brown, orange and yellow colouring are obtained from this plant.
- As a medicinal plant
![]() More information on goldenrod
More information on goldenrod