Contents
What is a rhubarb plant?
Characteristics of garden rhubarb (Rheum rhabarbarum)
Common English name: Rhubarb
– Spanish / Español: Ruibarbo, ruibarbo de jardín
Scientific name: Rheum rhabarbarum auct.
Taxonomic synonym: Rheum undulatum L.; Rheum franzenbachii Münter; Rhabarbarum verum Garsault
Family: Poligonáceas – Polygonaceae
Habitat: the origin of this plant is unknown, as it is believed to be derived from the species Rheum palmatum L. and Rheum rhaponticum.
In written records is the consumption of garden rhubarb in England in 1573, described by Tusser. From England, it was later exported to America.
Botanical description, varieties and species of rhubarb
It is currently cultivated in several countries as an edible vegetable, especially in the United States, the Magellan region and Eastern and Central Europe.
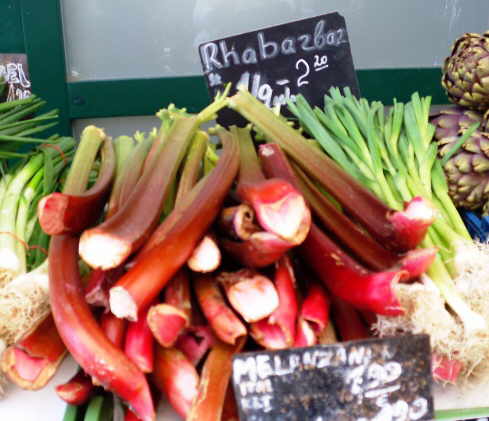

In the image: bunch of rhubarb at Naschmarkt market, Vienna
Botanical description of garden rhubarb
Botanical classification | |
Kingdom | Plantae – Plants |
Subkingdom | Tracheobionta |
Superdivision | Spermatophyta |
Division | Magnoliophyta or Angiosperm |
Class | Magnoliopsida or Dicotyledonous |
Order | Caryophyllales |
Family | Polygonaceae |
Gender | Rheum |
Species | R. rhabarbarum |
Garden rhubarb (Rheum rhabarbarum, Rheum undulatum L.) is widely known for its culinary qualities, while other varieties of Rhubarb are noted for their medicinal qualities, used in preparations with their dried rhizomes.
All kinds of rhubarb have similar therapeutic properties, although rhizome extracts of Chinese rhubarb are considered more therapeutic than garden rhubarb, intended primarily for food.
Rhubarb is a shrub grass of the polygonaceae family. It is often confused with a vegetable, although it really is not, but it is an herbaceous species related to buckwheat.
Perennial plant up to 3 meters. It remains productive when 5 years old, according to the cultivation methods used. For example, in the USA. Productive crops have been maintained for 12 years.
The subterranean stem of the plant is called rhizome. It is characterized by its horizontal growth below ground. It is yellow in its interior and brown in the outside.
From the rhizome emerges the system of tuberous reserve roots, which at the same time branch into numerous secondary roots.
The aerial part of the plant is formed by the leaves and the inflorescence.
Rhubarb leaves are basal (or radical) and caulinary. The first ones do not have petiole or this one is very short, whereas the other ones are great, They can measure up to 1 meter in diameter in some varieties. They are characteristically cordiform, lobed (5 to 7 lobes) and toothed. The petiole is semi-cylindrical, long, 2 to 5 centimeters wide. Its color varies between green and red. The nodal ocreas possessed by rhubarb are characteristic of the polygonaceae.
The petiole of each leaf is the only part that is used as food. They are acid and juicy, are harvested in spring. The blade of the leaves are TOXIC due to their high content in oxalates and anthraquinones, reason why they should not be consumed. More information on the toxic effects of intake of rhubarb leaves in the below listing.

The inflorescence is the highest part of the plant. The floral stem can measure up to 2 meters in height, and consists of tiny flowers that grow in the form of panicles. These flowers are creamy and monoecious. Rhubarb needs a vernalization process to flourish.
Vernalization is a usual cycle in many grains and seeds which consists of exposure to low temperatures to induce flowering, that is to say, a minimum amount of cold hours. In the case of rhubarb, these temperatures should be below 10 ° C – so that the opening of the flowers of the plant takes place.
Fruiting occurs in May-June of the third year of cultivation, in the northern hemisphere. This is a dry achene fruit with a trigonal, winged, reddish shape and approximately 1 to 1.5 centimeters in size.
The plant is characterized by losing all its leaves in winter (the aerial part), and again sprouting in spring. This is because of its subterranean stem or rhizomes, which allow it to conserve its nutrients during the cold and lie dormant underground until the climatic conditions are favorable to sprout.
Varieties of garden rhubarb
- Rheum rhabarbarum Victoria variety: Variety characterized by an intense red color, more bitter petioles. It is grown for food purposes. High oxalate content.
- Rheum rhabarbarum MacDonald variety: soft petiole, soft, bright and intense red.
- Rheum rhabarbarum variety Canada Red (Red Canada): very long petiole, thick, sweet-tasting stems.
- Rheum rhabarbarum variety Red Cherry: characterized by a succulent stem of intense red color both on the outside and its juice. Sweet variety with soft stems.
- Rheum rhabarbarum Valentine variety: variety of broad stems of dark red color. Highly valued for its attractive color in its gastronomic applications. It is not as acidic as other varieties. It has the least amount of juice.
*Related information: Rhubarb as food
![]() More information on rhubarb.
More information on rhubarb.