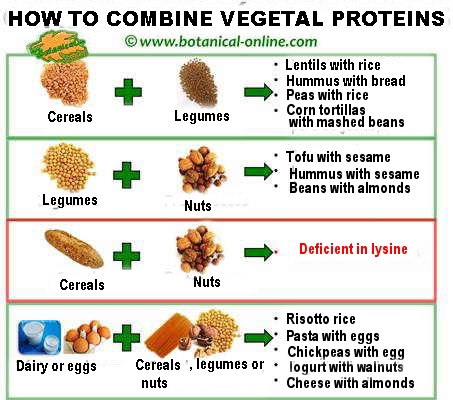
Contents
Properties of glycyrrhizin-free licorice
What is DGL or deglycyrrhized licorice?

Licorice preparations (Glycyrrhiza glabra L.) are currently being widely used for their different properties. It can be found in various forms, including capsules, tablets, pills, tinctures, dry cream, etc., that are purchased at pharmacies or herbalists.
It is used internally for its liver protective properties, for coughs, and to treat digestive conditions such as flatulence or slow digestions. It also has properties for heartburn, gastritis, and stomach ulcers.
The problem with long-term licorice treatments is that they have significant contraindications and their continued use has side effects. These adverse effects are due to a bitter component of the plant called glycyrrhizin.
Problems with licorice and contraindications of glycyrrhizin
The bitter principle known as glycyrrhizin can produce, in high doses or in continued use, adverse effects such as fluid retention, which in turn increases sodium retention and raises blood pressure, which can cause heart rhythm disturbances.
The adverse effects of glycyrrhizin could be fatal in cases of heart problems, heart disease, or if these preparations are taken by people with high blood pressure. Because it is a bitter principle, licorice preparations are also not safe for long-term use in people with stomach ulcers, gastritis, or heartburn, due to the bitter ingredients’ ability to stimulate digestive secretions.
Licorice without glycyrrhizin, deglycyrrhizinated licorice, or DGL (0.its acronym in English, Deglycyrrhizinated licorice), contains less than 1% glycyrrhizin. It is the only licorice preparation recommended for people with hypertension, and the safest to use for digestive ulcers and gastritis, as it does not contain this bitter principle.
However, DGL extract may not be completely free of glycyrrhizin (it contains <1%). So it is recommended to use it with caution, at the recommended doses. Consult your doctor if symptoms do not disappear or worsen.
Properties of glycyrrhizin-free licorice (DGL)
Glycyrrhizin-free licorice (DGL) retains many of the plant’s medicinal properties, as it contains all of its flavonoids.
- Stomach ulcer: The licorice flavonoids have antiulcer and antispasmodic properties, which stop the acid secretion of the stomach and improve digestion. They reduce acid secretions and increase the protective mucus in the stomach.
It helps prevent or treat stomach upset, indigestion, or other more serious bowel diseases, such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease. Its use appears to relieve constipation.
This property is very interesting for applying treatment in those cases where it is necessary to reduce stomach acids, such as heartburn, gastric ulcers, esophageal ulcers, stomach pain, or mouth ulcers. (Chew three glycyrrhizin-free licorice wafers about three times a day.)
- Antidepressant: Licorice helps combat depression. This property is influenced by the presence of several minerals such as calcium and magnesium, vitamin C, and the flavonoid isoliquiritigenin.
- Smoking habit: DGL licorice wafers make tobacco taste unpleasant.
Liquorice without glycyrrhizin is not suitable during pregnancy
Liquorice preparations are completely contraindicated during pregnancy due to its abortive, emmenagogue, and hypertensive effect, and for its estrogenic activity.
![]() More information on contraindications and toxicity of licorice
More information on contraindications and toxicity of licorice