Contents
- 1 How to grow eggplants
- 1.1 Eggplant cultivation tips
- 1.2 Eggplant characteristics
- 1.3 Eggplants – irrigation
- 1.4 Eggplants – uses
- 1.5 Eggplant-Care
- 1.6 Eggplants – Harvesting and conservation
- 1.7 How to store and preserve eggplants?
- 1.8 Eggplants – Pests and diseases:
- 1.9 Ecological insecticide to treat eggplant diseases and pests
How to grow eggplants
Eggplant cultivation tips
Eggplant characteristics
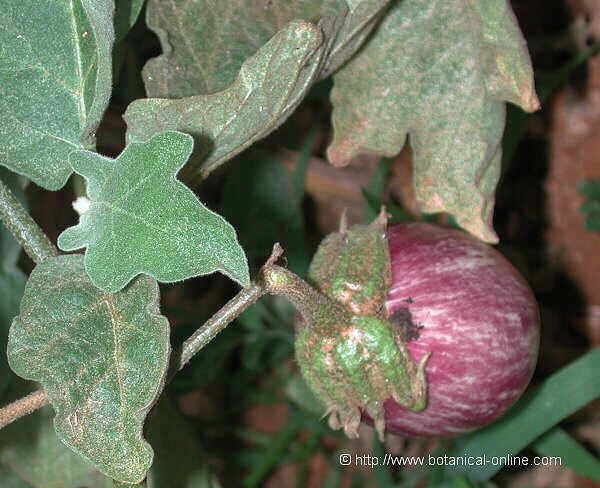

Eggplant or aubergine belong to the plant family of Solanaceae. It is a herb from 30 to 70 cm high .
Stems erect and hairy.
Leaves entire, pubescent gray-green oval with the presence of spikes in the vein of the same.
Flowers purple up to 4 cm in diameter, solitary or clustered in groups with chalice covered with bristles.
Eggplant fruits are berries usually elongated, purple color with white bands, although we find very different varieties of color, even color completely white or completely black varieties. Its size can reach over 30 cm but there are varieties that produce very small fruits that do not exceed 2 cm in length.
Its origin is usually located in Southeast Asia. Some will focus it in India.
Today, it is cultivated in most regions of the world.
 Eggplants – irrigation
Eggplants – irrigation
Eggplants need an abundant irrigation. They must be watered especially during the time when the fruits grow so that they have a proper development. During the warmer seasons, it is estimated that every day these plants need a quantity of approximately six liters of water per m 2.
Eggplants are suitable for growing in pots or containers. In this case we must bear in mind that watering should be very abundant and consistent so that the pot does not dry. It is important that the pot has good drainage underneath so the water does not accumulate in the roots.
Eggplants – uses
Eggplant is a plant that is cultivated for its fruits
Eggplant-Care
Among the main tasks of maintenance, we can mention the following:
- Staking: Like most vegetables, eggplant should be guided on rods, ribbons or other guardians to rise above ground and not to be subjected to moisture problems. On the other hand, placing the fruits and leaves most high allows plants to have greater ventilation. Eggplants should be tied to canes from the main stems when they reach 60 cm in height. We need to review either side shoots as they grow to tie these to them.
- Elimination of leaves: It is important to remove diseased or dried leaves and the excess of inner and lower leaves. This provides better ventilation, a greater amount of light and greater ease of collection and treatment of the fruit. It is important to perform this task during the days of low humidity and before watering, when the soil is somewhat dry. Otherwise, the wounds of the cuts could become infected.
- Pinching: when they reach 60 or 70 cm, trim the tops to encourage lateral development and give them a bushy appearance.
- Thinning of the fruit: It is important to clarify the fruits to avoid excessive fruiting, which would limit their size and quality. Usually tend to leave a maximum of five fruits per plant. Remove excess flowers, leaving only about 5 at the time that the fruit begins to swell.
- Weeding: The work of removing weeds is very important to prevent these consuming cultivation resources, such as water and nutrients. This work can be done manually or by means of herbicides.
- Maintaining soil moisture: Soil should be watered when needed. One way to ensure that soil moisture is more constant is padding it.
 Eggplants – Harvesting and conservation
Eggplants – Harvesting and conservation
The fruit harvesting is done between 110 or 170 days after sowing, when fruits are mature without being too old . This can be known because they have a shiny and smooth, with full color and smooth texture . If you pick them green, they will not have any flavor, whereas, if passed, they will become bitter.
At the time of picking-up, we must take into account that they are delicate fruits, very sensitive to shocks or abuse. Any impact is manifested by the appearance of skin spots.
Eggplants should be collected by hand, cutting with a sharp tool and clean it, leaving a free stalk a couple of fingers. Once cut, they will be stored in boxes, properly protected with paper backing and with the stems upward.
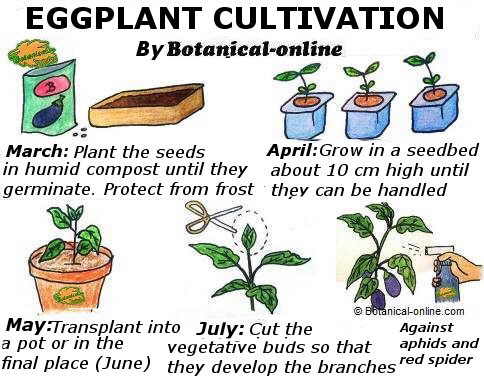
Summary drawing about the cultivation of eggplant. By courtesy of © dibujosparapintar.com
How to store and preserve eggplants?
Before taking them to market, they can be kept in cold storage for a week or week and a half at a temperature of about 4 or 5 degrees C.
At home they can be frozen in the refrigerator.
 Eggplants – Pests and diseases:
Eggplants – Pests and diseases:
The main pests that affect the eggplants are almost the same as those that affect tomatoes, that is to say:
- Lined click beetle
- Aphids
- Mildiu
- Powdery mildew
- Anthracnose
- Cucumber mosaic virus
- Tobacco mosaic virus
- Virus Y of the potato
- Virus X of the potato
In addition to these diseases, we should also consider the following:
- Etiolation: This occurs due to lack of light accompanied by a humidity too high during the growth phases. This plant produces very developed, lack of flowers and fruit deformity.
- Potato beetles: (Leptinotarsa decemlineata) they are beetles about 10 mm, characterized by the 4 yellow background black bands covering their elytra. The larvae have a round shape and orange. Both larvae and adults eat the leaves of the plants on which they live (mainly of potatoes, but also other plants of the same family as tomatoes or peppers).
To control them, insecticides or other more environmentally friendly procedures can be used, such as collection of adult beetles or the use of modified genes from the bacterium Bacillus thuriengiensis.
In the latter case, the Bt gene of this bacterium is modified to incorporate into the plant. Once the genetically modified Bt gene, the plant develops toxins that are ingested and attack the predator’s digestive system which is designed for without affecting other creatures, including humans.
Ecological insecticide to treat eggplant diseases and pests
The following ecological recipe can be very suitable to treat most of your eggplants problems:
Treatment against garden pests with garlic |
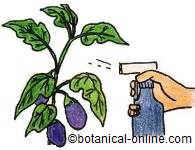 You need 1 head of garlic (50g aprox.) And 5 liters of water. You need 1 head of garlic (50g aprox.) And 5 liters of water.Chop the garlic and let it marinate in 5 liters of water for about 1 week, in the fridge. Then the mixture is strained. Dilute in half: 1 liter of mash with 1 liter of water. Place in a container to spray on the plants. It is effective against most pests and fungal diseases, aphids, spider mites, etc. |
![]() More information on eggplant.
More information on eggplant.

 Eggplants – irrigation
Eggplants – irrigation Eggplants – Harvesting and conservation
Eggplants – Harvesting and conservation