Contents
- 1 What is a heather plant?
- 1.1 Characteristics of heather (Calluna vulgaris (L.) Hull)
- 1.2 Habitat: where to find heather?
- 1.3 Description of common heather
- 1.4 Active components of Calluna vulgaris
- 1.5 Which part of the heather is used medicinally
- 1.6 Dosage of common heather
- 1.7 TRADITIONAL USES OF HEATHER
- 1.8 Heather industrial and home uses
What is a heather plant?
Characteristics of heather (Calluna vulgaris (L.) Hull)
Common name in English:
Heather, common heather, ling
Scientific name: Calluna vulgaris (L.) Hull
The name of the genus “Calluna” comes from the Greek “Καλλύνω” kallúnô, which means “to adorn, beautify, decorate”
“Vulgaris” comes from Latin and means common, the species within the genus calluna that appears more frequently.
Synonyms: Calluna vulgaris var. pubescens W.D.J.Koch; Erica vulgaris var. alba Weston; Calluna sancta Gand.; Calluna sagittifolia var. hirsuta Gray; Calluna pyrenaica Gand.; Calluna oviformis Gand.; Calluna olbiensis Albert; Calluna erica var. condensata (Lamotte) Rouy; Calluna erica proles olbiensis (Albert) Rouy; Calluna erica proles beleziae (Rouy); Calluna brumalis Gand.; Calluna beleziana Rouy; Calluna atlantica Seemen; Calluna alpestris Gand. Ericoides vulgaris (L.) Erica vulgaris L.; Calluna sagittifolia Gray; Calluna erica DC.; Calluna beleziae Rouy; Calluna erica var. hirsuta (Gray) Rouy in Rouy & Foucaud; Calluna sagittifolia Gray; Erica sagittifolia var. villosa Stokes; Erica sagittifolia Stokes.
Family: Heather family (Ericaceae)
Habitat: where to find heather?
Natural of Europe, America and North Africa. In Europe, it can be found in all countries except Albania, Bulgaria, Hungary and Turkey. It lives in marshy areas, peat bogs, upland heaths, moors, dunes, open forests of pines or oaks, on dry or humid but acid soils, from sea level up to 2800 meters. It prefers a sunny or light shade exposure.
It is the dominant plant in heaths (lands where bushes abound, especially heathers and brecines) and moorlands (high and erratic lands). It is the dominant species in the cold moorlands of the United Kingdom and the north of Europe, abounding a lot in the Norwegian cold and barren lands, to the point that this is the national flower of Norway.
Common heather is the only species of the genus Calluna, related to the genus Erica (Erica multiflora, Erica tetralix… etc). The genus Calluna is distinguished from the genus Erica mainly by the calyx of the flower. In Calluna the calyx is petaloid and has the same color as the corolla. Species of the genus Erica have a green calyx.
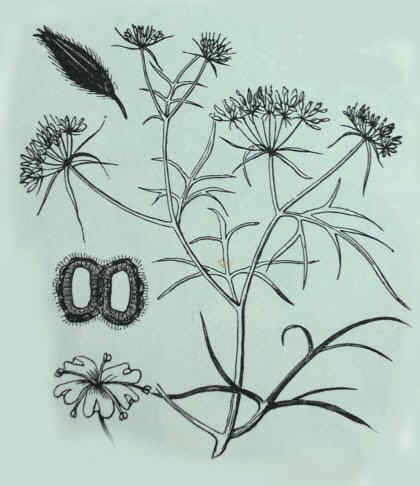
Description of common heather

Illustration of common heather ( Calluna vulgaris )
Shrub of Ericaceae family, 50 or 60 cm high, more rarely about 1 m
Stems abundant and branched, generally twisted and very rigid, hairy or glabrous.
Very small triangular leaves of 1 to 2 mm, sessile, imbricated, arranged in four vertical rows. When autumn arrives, they become brown or pale purple.
Bell-shaped flowers, gathered in compact inflorescences; Pale purple, or pale pink (more rarely, white) very small, with tetralobulate calyx, the same color as corolla and longer than this (4 mm). False calyx formed by 4 green bracts
Fruits in capsule of 2 to 2, 5 mm, with four lobes, with a seed inside each one of them.
Active components of Calluna vulgaris
- Glucosides: Arbutin (0.5 to 1%), inulin, ericolin, glucose
- Tannins
- Enzymes: Arbutasa
- Acids: chlorogenic, vanillic, fumaric, citric, gentisic, paracoumaric, parahydroxybenzoic, syringic, ursolic, etc.
- Flavonoids: quercetin, myricitrin.
- Coumarins: escopoletol, esculetol
- Antioxidant pigments: Anthocyanidins (delphinidin, leucodelphinidin, cyanidin, myricetin)
Which part of the heather is used medicinally
Curative properties have to be found in the floriferous summits (the upper set of leaves and flowers). Common heather flowers should be collected from late summer until fall.
Once collected, they should be dried in the shade in a dry place.
Once dried, they should be stored in paper or cloth bags in a cool, dry place, protected from light.
Dosage of common heather
- Infusion: One and a half tablespoon of dried flowers per cup of water. Let stand 10 minutes
- Decoction: Boil 1 teaspoon and a half for 10 minutes per cup of water
- Mother tincture: 30 drops in three daily doses
TRADITIONAL USES OF HEATHER
- Healing properties: Traditionally, heather plants have been used in the preparation of herbal teas. In Germany and Austria they have been widely used for the treatment of diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract.
Italian physician and naturalist Pietro Andrea Gregorio Mattioli (1501 1577) describes common heather as a suitable plant for the treatment of urinary grit. Different cultures have made use of it for its diuretic, depurative, antiseptic, astringent, antidiarrheal, healing, antitussive and tranquilizer properties.
- Magical properties: White varieties of common heather are considered magical in Scotland. It is considered that this plant gives good luck to couples, so heather twigs are usually included in the wedding bouquets to wish a good future to the couple.
- Food for livestock and wild animals: In cold areas of Scotland and northern Europe deer and sheep feed on the exposed parts of this plant when snow covers the lower grass.
Similarly, the Scandinavian lagopoda (galliform birds) eat the shoots and fruits of these plants. The larvae of many butterflies feed on the leaves of heather, including that of the beautiful Small Emperor Moth (Saturnia pavonia). Of all the insects, the one that takes advantage of this plant is the so-called heather beetle (Lochmaea suturalis), which, in benign times, causes real havoc in this plant.
Heather industrial and home uses
- Heather to aromatize beer: For a long time, especially in the Middle Ages and until the hops were discovered, heather was used as a flavoring ingredient in brewing.
- Heather for dyes and tannins: With heather a yellow dye is obtained. Tannins are extracted from the bark.
- Heather to make brooms, ropes, baskets… etc: As stated above, this plant has been used in the manufacture of brooms, but its domestic uses go much further and with this plant baskets, ropes, material for mattresses, insulation for floors, etc are made.
- Heather for vegetable roofs: In areas where this plant abounds, it is used as a vegetation cover, just as other different plants are used in other areas (cane, reeds, or palm leaves, for example).
- Heather, honey plant: Heather is very rich in nectar, so it easily attracts bees, butterflies and moths. The nectar of these flowers is used by bees to make honey (More information about heather honey)
- Heather, garden plant: There are over 400 varieties of heather, a plant widely used in gardening (More information)
![]() More information on heather
More information on heather