Contents
- 1 How to grow kiwi fruits
- 1.1 KIWI CULTIVATION TIPS
- 1.2 Characteristics of kiwi plant
- 1.3 Description of kiwi plant
- 1.4 GROWING CONDITIONS FOR KIWI FRUITS
- 1.5 Optimal climate for growing kiwis:
- 1.6 Good soil for kiwi
- 1.7 Kiwi Irrigation
- 1.8 How to plant kiwi from seed
- 1.9 Kiwi cultivation requirements
- 1.10 Kiwi pollination and bloom
- 1.11 Kiwi fruit harvesting
- 1.12 Control of diseases and pests of kiwi crops
How to grow kiwi fruits
KIWI CULTIVATION TIPS
Characteristics of kiwi plant

Kiwi or Chinese gooseberry is plant vine (Actinidia deliciosa = Actinidia chinensis), native to eastern China, from Zhejiang area. In this region, the fruits of this plant are consumed as wild fruits, and it was not until 1906 that spread to New Zealand, where the plant is perfectly adapted to the climate and began to grow.
New Zealand also gave the name to the kiwi fruit, due to its resemblance to the animal also called Kiwi.
There are many varieties of kiwifruits: Actinidia chinensis var. hispida was initially the most cultivated one. Currently, the Hayward variety is the most commercialized.
It is a plant with special cultivation requirements, needing specific care such as favorable weather conditions, suitable soil, well-drained, fertile, with a lot of moisture and nutrients.
Description of kiwi plant

Kiwifruit is a shrubby vine up to 8 m tall.
Woody stems with tendrils that latch onto the support.
Oval, alternate, long stalked leaves.
Initially white female flowers, later yellow, The male flowers are usually smaller.
The fruits are berries gathered in clusters. They have a brown leather hairy cover and are oval shaped; its flesh is green (because it contains chlorophyll)
Seeds, tiny and black, arranged in a circle about the center of the fruit.
Kiwi is a dioecious plant: there are male plants and female plants, and both are needed for a crop to produce fruit.
GROWING CONDITIONS FOR KIWI FRUITS

Optimal climate for growing kiwis:
– Plant in full sun or semi-shade
– Grows well in subtropical, temperate climates without extreme temperatures in winter. It does not tolerate frost, and must be protected from cold in winter.
– Optimal temperature: 24 º C to 8 º C day and night. Above 35 ° or below -12 º C temperatures seriously damage it.
– Protect from wind, it will be necessary to use a windbreak.
Good soil for kiwi
– Soil type: sandy loam or loamy, deep, moist, well drained and slightly acidic with a pH 5.5 to 7.2.
– Drainage: Avoid water logging or flooding water!
– It does not tolerate soil salinity.
Kiwi Irrigation
– Most crops that have problems are due to irrigation.
– Kiwi fruit is very sensitive to water flooding, because this condition favors the occurrence of root diseases.
How to plant kiwi from seed
How to obtain kiwi seeds?

You can get seeds from ripe fruit purchased in spring, usually germinate well. Do as follows:
- Squeeze some kiwis with a juice manual machine.
- Strain the juice through a sieve to remove seeds.
- Place the the seeds, mixed with moist fertile soil in a plastic bag or in a covered seedbed, and keep it in refrigerator for 2 weeks
How to sow kiwi seeds?
- Although they have not germinated yet, seeds are sown in a seedbed or container.
- Sowing depth should be at most twice the size of the seed (as a general rule to all soils). In the case of kiwi, it will not exceed 23 mm. (That is, put the seeds on the soil and “sprinkle” a little dirt on it).
- The plant will germinate about 23 weeks later. When measuring about 10 inches, they can be transplanted to a larger pot or planted out if weather and soil conditions are optimal.
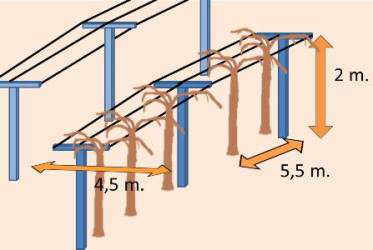
- Planting distance: 5.5 m. between plants and 4.5 m. between rows.
Kiwi cultivation requirements
Kiwi is a plant with climatic and nutritional needs that can not be successful if not properly cared for. It has even been reported cases of large crops and high cost, which have not been successful due to the special requirements of this plant.
- Sluch and dug: It will be very important to remove all the soil well for oxygenation. The soil must not become compacted, which could hinder the development of root and water penetration (deep digging is not necessary for very light or thin soils, then just do a surface cleaning with a rake).
- Prepare stakes and wires: These vines are generally planted to be entwined in wires supported by stakes in “T” (see drawing below)., A male plant should be plant each 8 plants. the male plant should be placed next to stake, females can be planted with the help of a tutor, like a reed. As they start trellising, plants should be secured to the tutors with the help of a cord or ribbon.
- Pruning: After the first year, they must be subjected to an initial pruning so as it can branch into two primary branches, or into scaffold branches from the second year on. It should Branches should be tied to the the tutor to make them grow as straight as possible. All pruning will be one in full winter, while plants remain dormant.
Kiwi pollination and bloom
Pollination of flowers is done by insects and wind. It is a very important point because the fruit size is determined by pollination. Owning a hive of bees in the crop helps improve tree fruit production, since these animals transport pollen from male to female flowers favoring fruiting. Normally mesh placement (at a height that does not touch the branches) to increase pollination by these insects.
Being a dioecious plant, the presence of male and female kiwi plants in a crop is necessary. 10 female – in general, a male plant crop per 5 is recommended.
Kiwi fruit harvesting

Kiwis will begin to produce good amounts of fruits 4 years after having been planted. On average, a fruit shrub of this kind produces about 20 kg. (Approximately 150 fruits) per year, but it can reach 80 kg. in some cases.
Kiwifruit is a climacteric fruit, which can ripen once picked.
Fruits can be harvested almost to the point to finish ripening off the tree, so will be easier to transport and trade. Ripening can be accelerated by placing the fruit in a bag with ethylene gas, such as a mature apple.
Control of diseases and pests of kiwi crops
- Bacterial canker of kiwi or PSA ( Pseudomonas syringae pv r actinidiae.): It is the main threat affecting kiwi crops. One of the first measures of prevention is to acquire seed quality to ensure that it is free of PSA. It can actually cause great losses. it is aggravated by moisture (meshes crops are more susceptible)
- Cochineal (Pseulacaspis pentagona)
![]() More information on kiwi.
More information on kiwi.