Contents
WHAT IS CUMIN PLANT LIKE?
Cumin characteristics (Carum carvi)
Relative of caraway (Carum carvi), cumin is also erroneously called Roman caraway , oriental caraway , Egyptian caraway or Turkish caraway.
Common English name: cumin
* See: Cumin in other languages
Scientific Name: Cuminum cyminum L.
Taxonomic synonym: Cuminum officinale Garsault, Cuminum odorum Salisb., Cuminum hispanicum Mérat.
Family: Apiaceae or Umbelliferae
Where is cumin from?
Cumin is a native plant of Mediterranean region. It is believed to have originated in Turkestan, from where it spread, in ancient times, to Egypt, Ethiopia and the Mediterranean coast.
Today we can find cumin on the Mediterranean coast, India, Iran, Indonesia and China.
Botanical description of Cumin
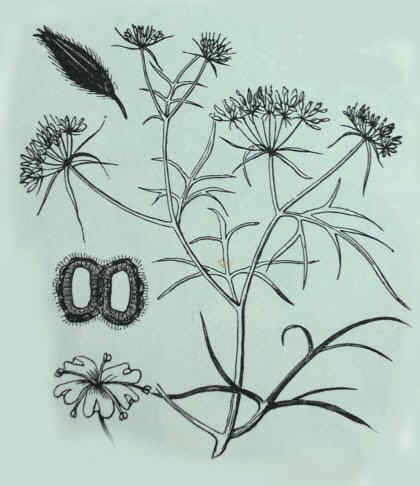
Botanical illustration of cumin plant. At the bottom left of the illustration, a detailed flower.
Cumin (Cuminum cyminum) is an annual herbaceous plant of the Apiaceae family characterized by presenting its flowers arranged in umbels. The umbel is a type of inflorescence, similar to an inverted umbrella, which is formed because all the flower stalks are joined to the stem by the same point.
The cumin plant is of Mediterranean origin. It has an erect stem, little branched, not very tall, from 20 to 50 cm (up 80 in some cases). The inner core of the stem is white.
Cumin leaves are arranged alternately to the stem, petiole bonded. Hairless, elongated and divided. This plant is easy recognized because its foliage is divided into filiform segments. They are very similar to those of dill, which belongs to the same botanical family as cumin.
The inflorescence is a terminal umbel which have tiny hermaphrodite flowers, white or pink. Each umbel may contain between 3 and 5 radios.
The fruit of the plant is classified among the nuts and it is a diachene. They are ash brown, oval, narrow and pubescent, from 5-6 mm long and 1-2 mm thick.
Used parts of cumin
- Seeds or fruits: small fruits are used as a spice, (only in blends like curry and chili), and phytotherapy.
- Essential oil: is used in aromatherapy, perfumery and as a flavoring additive.
Medicinal uses of cumin
Eupeptic, digestive, carminative, galactogogue, anthelmintic o, spasmolytic, slightly hypoglycemic, sedative. (More information in the listing below)
*See: Cumin composition
Botanical classification of cumin | |
Kingdom | Plantae |
Subkingdom | Tracheobionta |
Superdivision | Spermatophyta |
Division | Magnoliophyta |
Class | Magnoliopsida |
Order | Apiales |
Family | Apiaceae |
Subfamily | Apioideae |
Tribe | Scandiceae |
Subtribe | Daucinae |
Gender | Cuminum |
Species | Cuminum cyminum |
![]() More information on cumin.
More information on cumin.








