Contents
- 1 Benefits of polyunsaturared fatty acids
- 1.1 CHARACTERISTICS OF POLYUNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS
- 1.2 Types of polyunsaturated fatty acids
- 1.3 Essential fatty acids
- 1.4 Why are they essential fatty acids?
- 1.5 Derivatives of essential fatty acids omega 3 and omega 6
- 1.6 Table of common polyunsaturated fatty acids
- 1.7 Foods rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids
Benefits of polyunsaturared fatty acids
CHARACTERISTICS OF POLYUNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS
Polyunsaturated fatty acids are a type of fats that are characterized by the presence of two or more double bonds between the carbon chains that make up the fatty acid.
 Photo of a detail of some cookies composition. The classification of fats can be distinguished according to whether they are saturated, monounsaturated or polyunsaturated. |
Some polyunsaturated fatty acids are essential, meaning that the human organism is unable to synthesize them and have to be fed through.
Essential fatty acids are polyunsaturated fats omega 3 (linolenic acid) and omega 6 (linoleic acid).
Essential fatty acids play an important role for the nervous system, cardiovascular health and have a major role in diseases such as arthritis, hyperactivity or lupus.
Types of polyunsaturated fatty acids
The most common polyunsaturated fatty acids in foods are usually those containing 18, 20 and 22 carbons.
- From the family of omega 6, we found linoleic acid and arachidonic acid (AA).
- From the family of omega 3, we found linolenic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). They are designated, respectively, with the following nomenclature:
- C18: 2, linoleic acid
- C18: 3, linolenic acid
- C20: 4, arachidonic acid (AA)
- C20: 5, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- C22: 6, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
The first number indicates the amount of fatty acid carbons. The preceding number designates the number of double bonds or unsaturations it contains. In this case they are polyunsaturated and consequently, the value is greater than one.
Essential fatty acids
Within the group of polyunsaturated fatty acids, there are only two fatty acids that are essential for our body.
These essential fatty acids are linoleic acid (18: 2) and linolenic acid (18: 3), which are called omega 6 and omega 3, respectively.
The structural difference between these two types of omega fatty acids lies in the location of the first double bond they contain in their carbon chain. Being at carbon 6 and at carbon 3, respectively.
Why are they essential fatty acids?
Our body is able to make carbon structures with double bonds from carbon number 9, so, as these two fatty acids contain one and two double bonds (respectively) prior to carbon 9, our body can not synthesize them.
For this reason, they are considered essential and have to be ingested through our food to obtain them, not to generate nutritional deficiencies or synthesis.
All other fatty acids can be synthesized through other substrates in our body, therefore, they are not essential.
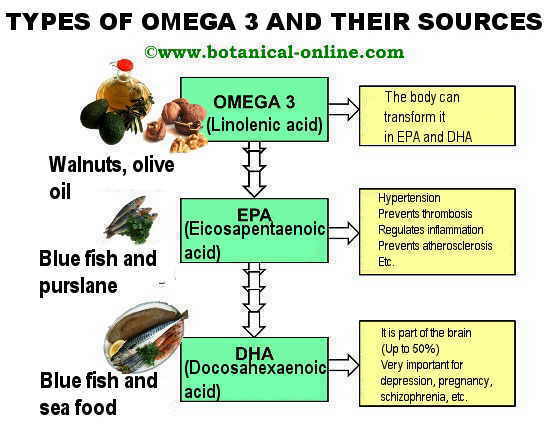
Derivatives of essential fatty acids omega 3 and omega 6
Through ingestion of essential fatty acids, our body can synthesize other polyunsaturated fatty acids from longer chains. Among these polyunsaturated fatty acids of longer chains, the most relevant are:
- C20: 4, arachidonic acid (AA)
- C20: 5, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- C 22: 6, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
Bluefish directly contains EPA and DHA fatty acids, and cod liver oil supplements are very effective when the benefits of omega 3 are desired. By directly providing EPA and DHA, they save the body from having to make this transformation.
Summary sheet with the different types of omega 3, functions in the body and its sources in the diet, Produced by © Botanical-online |
Table of common polyunsaturated fatty acids
| Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid | Name | Vegetal food containing it | Animal feed containing it |
| C18:2 | Linoleic acid (OMEGA 6) | Most of vegetal oils | |
| C18:3 | Alpha-linolenic (OMEGA 3) | Sunflower oil, corn oil, soybean oil and canola oil or rapeseed oil, walnut oil, flax,… Nuts | |
| C18:3 | Gamma-linolenic (OMEGA 3) | Borage oil and evening primrose oil | |
| C20:3 | Dihomo-γ-linolenic acid (OMEGA 3) | Fish oils | |
| C20:4 | Arachidonic acid (OMEGA 6) | Pork fat, poultry fat | |
| C20:5 | Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) | Fish oils | |
| C22:5 | Clupanodonic acid | Some types of algae and fish oils | |
| C22:6 | Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) | Fish oils |
Foods rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids
Table of foods rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids
| Per 100g. | Polyunsaturated fatty acids | |
| Linoleic acid Omega 6 (g.) | Linolenic Omega 3 (g.) | |
| Sunflower oil | 63,2 | 0,1 |
| Soybean oil | 51,5 | 7,3 |
| Sunflower seeds | 37,4 | 0,08 |
| Olive oil | 9,1 | 0,85 |
| Walnuts | 34 | 8 |
| Hazelnuts | 8,5 | 0,11 |
| Peanut oil | 32 | 0 |
| Palm oil | 10,1 | 0,3 |
| Almonds | 12,6 | 0,26 |
| Corn oil | 50,4 | 0,9 |
| Cashews | 7,2 | 0,15 |
| Peanuts | 12,8 | 0,35 |
| Avocado | 1,7 | 0,17 |
| Pistachios | 7,9 | 0 |
| Coconut oil | 1,8 | 0 |
| Dried grated coconut | 1,5 | 0 |
| Corn margarine | 31,3 | 0,65 |
| Tunna in vegetal oil | 5,3 | 0,13 |
| Cod liver oil | 2,6 | 1,10 |
| Hard cheese | 0,44 | 0,25 |
| Fresh cheese | 0,43 | 0,46 |
| Butter | 1,8 | 0,53 |
| Veal | 0,35 | 0 |
* Related information:
![]() More information on fats.
More information on fats.