Contents
Why are plants important?
What are plants?
Plants are living organisms belonging to the vegetal kingdom that can live on land or in water.
There are over 300,000 species of plants, of which more than 250,000 produce flowers. Unlike animals, that need to eat already processed food, plants are able to produce their own food through a chemical process called photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is basically the production of sugar from CO2 (carbon dioxide) minerals and water (H2O) with the help of sunlight.

Resulting from this process is oxygen, a waste product that comes from the decomposition of water. Oxygen, which is formed by the reaction between carbon dioxide and water, is expelled from plants through the stomata of the leaves. Photosynthesis needs the energy that the plant takes from the sun.
Plants have many different forms. Some are called trees, others as known as herbs, others have a bushy form, some are known as lianas or simply as flowers. According to its height, if they are softer or harder or how we use them, etc, they are called with different names.
Importance of plants
Plants have had and still have a key role in the history of life on Earth. They are responsible for the presence of oxygen, a gas needed for most organism who currently inhabit our planet and need it to breathe. But this was not always so. At first, the earth’s atmosphere had almost no oxygen and was particularly rich in carbon dioxide (CO2), in the form of water-steam (H2O) and nitrogen (N). This atmosphere would be unbreathable for most species that today need oxygen to live.
The first living things did not need oxygen to breathe. On the contrary, this gas was a poison for them. It was more than 2000 million years ago when certain bacteria, together with plants, began to initiate the process of photosynthesis, transforming the atmosphere and making it habitable for most today living organisms.
Evolution of plants

Plants continued to evolve, adding oxygen to the atmosphere. They were abie to develop seeds. Plants that produce fruits are called Spermatophyta. The most primitive ones don’t have the seeds confined inside the fruits and are known as Gymnosperms or ” plants without flowers”. The most highly evolved plants are called Angiosperms or ” flowering plants”. They produce seeds shut in fruits.
Plants have contributed and go on contributing to create the right conditions for life on Earth to be possible. Thanks to the living creatures that produce oxygen, living organisms can breathe. Also, these organism have also contributed to the formation of ozone, a gas produced by the action of sunlight on oxygen. Ozone creates a layer in the atmosphere that protects us from harmful ultraviolet rays.
Another consequence of photosynthesis is the reduction of carbon dioxide, a gas that, by accumulating in the atmosphere, retains heat from the sun’s rays and causes the fatal famous “greenhouse effect”.
Plants have protected us for many millennia from “global warming” by absorbing the excess of carbon dioxide. Unfortunately, the burning of fossil fuels has increased its levels in such a way that plants themselves, progressively decreasing in number and variety, are not longer able to solve the problem of a planet which is getting increasingly hot.
Plants at the base of the food chain
Life on earth depends on plants. Humans, like other animals, can not feed themselves. Directly or indirectly, what they eat comes from plants.
Plants are important for having changed the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere. Plants are also important because they are able to develop their own organic matter (sugars, fats, etc.) from simple inorganic elements (minerals and water), something that can only be achieved by plants and other lower organisms (algae and some bacteria). These piants and organisms are called primary producers.
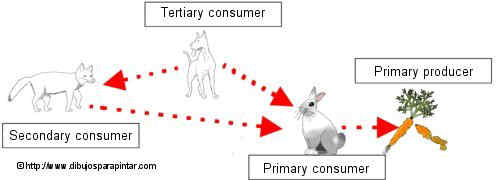
All the other living organisms on earth feed on organic matter produced by plants and some lower organisms, First, the primary consumers or herbivores that incorporate food in their bodies produced by plants. For example, a rabbit eats the carrot or a crab larvae consume the tiny plant organisms that float on water. Many living creatures feed on hervivores. they are called carnivores or consumers.
Some carnivores (Primary consumers) are eaten by other carnivores (Secondary consumers) which can be eaten by another ones (Tertiary consumers). A wild rabbit in the country can be eaten by a fox and a wolf or a dog can also eat the fox or even the rabbit. At the sea water, the larvae of crabs are eaten by sardines that are eaten by tuna.
Plants and food production
Humans depend, directly or indirectly, from plants. When we eat animal flesh, it comes from an animal that has been fed on grass. When we eat plant food, these are produced directly by plants. Million people around the world can be sustained on plants producing cereals,. This is the reason why wheat is the most important food in the western world, corn in many parts of America, or rice has become the first Asian food.
Other plant products are essential for human nutrition. Some tubers are of paramount importance, such us potatoes which are eaten almost anywhere, or cassava, which is a staple food in tropical areas.
Plants produce fruits, rich in carbohydrates, vitamins and fiber. The importance of fruit in the human diet has been recognized since remote times, to the extent that ancient people referred to it as “food of the gods” and granted it divine or magic properties. Bananas are the fourth most important type of food in the diets of developing countries after rice, wheat and maize. Oranges are the most consumed within the fruits.
Plants provide us with vegetables, rich in vitamins and minerals necessary for health maintenance. Lettuce, tomatoes, onions, carrots, etc.. are part of our regular salads. Spinach, cabbage, artichokes are also present in the diet of many people and provide essential food in the Mediterraneah Diet.
Nuts are a source of vegetable fat. They provide healthy calories and abundant minerals. Hazelnuts or almonds are very commonly used. Other plants also provide fat such as margarine from corn, and edible oils such as olive oil, sunflower oil or soybean oil.
We also obtain many well known drinks from plants, such as wine, that is produced from grages, beer, we get from barley with the addition of hops. Coffee or tea or other tisanes are also obtained from plants.
We must also take into account a whole range of products that are part of the food industry which derive from plants.
Plants and industry
Many industrial products derive from plants. Among the many industrial uses of plants, we can mention the following: wood for furniture, beams, doors, etc., paper pulp, fibers such as hemp, cotton, linen, etc., wood or coal; industry uses components such as tannin for tanning leather, pigments and varnishes, soaps, perfumes, shampoos, essential oils for the cosmetics industry; rubbers, lubricants, plastics for the automotive industry.
Medicinal and poisonous plants
The properties of medicinal plants have been used since ancient times to cure diseases. At present, in technologically advanced countries like the United States, an estimated 60% of its population use medicinal plants to combat certain diseases.
It is also increasingly recognized the importance of plants in the maintenance of health, up to the point that sometimes the line between food and medicine is very thin. Garlic is a world-renowned species, but at the same time, it is one of the best natural antibiotics. Plants play an important role in disease prevention.
Plants are our food and can also be our natural medicines, but many plants can be potentially fatal. Plants used in appropriate doses have healing properties, but larger amounts are converted into potent poisons.
(More information about Importance of medicinal plants)
Cultivation of plants

The discovery of agriculture or cultivation of plants is dated over 9000 years ago in the valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates, in a zone which would occupy the area that today belongs to the countries of Iraq, Syria and southern Turkey. Later, about 7000 years BC, it was developed in the valley of the Nile
The discovery of agriculture was a giant step for mankind. Men managed to free themselves from the daily effort of hunting or searching for food. So far the men were nomadic, ie they could not live on a fixed site. Agriculture allowed the man became sedentary, or to live in the same place.
Agriculture allowed to produce and store food, which facilitated the distribution of work. While some workers might work the land, others might focus on other duties. This enabled the birth of Culture and Civilization.
At present, almost 50% of the world’s workers are engaged in cultivation of plants. Agriculture continues to nurture mankind and is virtually the only direct or indirect source of food production. Only villages hidden deep in the forests remain primitive, using hunting and gathering methods as a means of livelihood.
Besides food, plants are also grown in gardens for its beauty. The role of minigardens in large cities as a way of raising vegetables is also becoming increasingly more important.
![]() More information about plants
More information about plants