Contents
(Litchi chinensis= Nephelium litchi)
CHARACTERISTICS OF LYCHEE
Common English name: lychee, lichee, liechee, li zhi, laichi, litchi, , liche, lizhi,Chinese nut,
Common name in other languages:
Botanical classification | |
Kingdom | Plantae – Plants |
Subkingdom | Tracheobionta |
Superdivision | Spermatophyta Seed plants |
Division | Magnoliophyta or Angiosperm (Flower plants) |
Class | Magnoliopsida or Dicotyledonous |
Order | Sapindales |
Family | Sapindaceae |
Gender | Litchi |
Species | L. chinensis |
– Spanish / Español: lichi, litchi, leché, mamoncillo chino, cereza de la China, ciruela china, avellana china, nuez china.
– Catalan / Català: litxi
– Galician / Galego: licheiro
– Portuguese / Português: lechias, uruvaias
– Italian / Italiano: litchi, ciliegia della Cina
– Romanian / Română: Lici
– French / Français: litchi, letchi
– German / Deutsch:Litschi, Litschibaum, Litchibaum, Zwillingspflaume
– Polish/ Polski: Liczi chińskie
– Dutch /Nederlands: Lychee
– Norwegian /Norsk bokmål: Litchi
– Finnish /Suomi: Litsi
– Swedish /Svenska: Litchi
– Turkish / Türkçe: Liçi
– Русский / Russian: Кита́йские ли́чи
Etymology: The term “lychee” comes from the Chinese “Lee Chee”, which means “donor of the joy of living”. The lichi is an emblematic fruit and highly valued in the Chinese food, where it originates.
Scientific name: Litchi chinensis Sonn. = Nephelium litchi Cambess.
Other taxonomic names:
– Scytalia chinensis Gaertn.
– Dimocarpus litchi Lour.
Family: Sapindaceae
Origin: Cultivated in Southeast China (Canton Province or Kwangtung) for more than 40 centuries, although its true origin could be from India.
Habitat: it grows in warm and temperate climates, tropical and subtropical regions.
Distribution: It is currently grown in many regions of Asia (Israel, Indochina, India, China, Nepal, Thailand, Vietnam, Taiwan, southern Japan, Philippines and Indonesia), Oceania (northwest Australia), East Africa (Madagascar, Mauritius, Reunion, Zimbabwe), America (Mexico, Brazil, Hawaii, Florida), Spain (Europe) and some Pacific islands.
Description of lychee tree
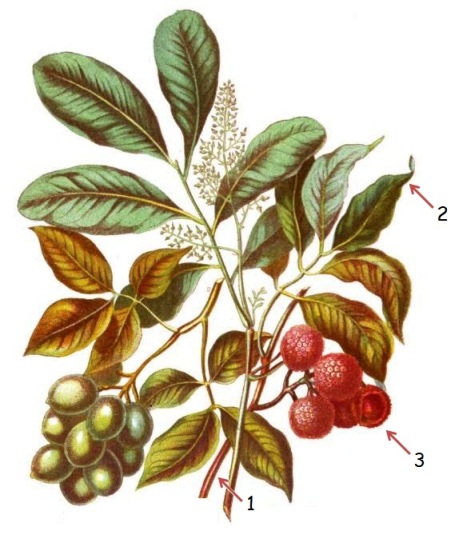 In the image: botanical illustration of lychee. The branch of lychee (1); Elliptical and pointed leaves (2); and fruits, which grow in clusters (3)..
In the image: botanical illustration of lychee. The branch of lychee (1); Elliptical and pointed leaves (2); and fruits, which grow in clusters (3)..Lichi (Litchi chinensis) is a perennial, rounded-stemmed fruit tree, measuring between 3 and 6 (up to 10m) in height.
The trunk is erect, rough, with brown bark and very branched.
The leaves are alternate and compound, 2-4 pinnate and elliptic-oblong, with acuminate apex and attached to the branch by petiole. Between 12-20 cm. long by 2-6cm. wide, smooth, bright and dark green obove and greyish green on the reverse. Young leaves can vary between yellowish green or bronze color.
The inflorescence of this tree are colorful clusters of flowers, growing from the axils of the leaves or the terminal part of the branches. Lichee lowers are pollinated by insects, such as bees (entomophilic pollination).
Flowers are polygamous, meaning that the tree has three types of flowers: male, female and hermaphrodite. Apetalous corolla (without petals), fleshy disc with 4-6 sepals, androceus with 8-10 stamens (often not producing pollen), ovary in 2-3 cells (of which only one develops the seed).
Lychee fruit is a drupe, better known as lychee, in a heart-shaped form, between 3 and 5cm. diameter. The pericarp of the fruit (“the skin”) is thin, hard, brittle and with numerous conical protrusions, pink, red or, in some varieties, green. The edible part of the fruit is a pulpy, translucent white pulp.
Botanically, the lychee pulp is called aryl, as it is formed from cells of the funiculus (the peduncle of the seed), and grows enveloping the seed.
The seed is dark brown and bright, between 1 and 2cm; 1-1,2cm. wide. It is possible that some lychees we buy have a very small seed, this is because they try to create varieties with little seed volume, so that there is more edible pulp.
Although some may confuse it with its hard shell, lychee is not a dry fruit, since its seed is not edible.
Used parts of lychee
Fruit: The fruit is harvested for food purposes. It has a mild, sweet and slightly acidic flavor, which is taken in snacks or as a dessert. It is the protagonist of some culinary elaborations, such as cakes, tatin, liqueurs, ice cream, juices, sorbets, etc. We can find them in the market fresh, dried, frozen, in juices and canned.
Seeds: From the seeds soaps and campuses for the hair are obtained.
Flowers: They are used by bees to produce honey (Melliferous plant)
Wood: In China, lychee wood is used for the production of furniture.
Ornamental: This tree is cultivated in some areas for the decoration of gardens or in cities, because it is perennial and always remains green. Its red fruits are very decorative.
Perfumes: The aroma of lychee, which can remind us about rose water, is used in perfumery.
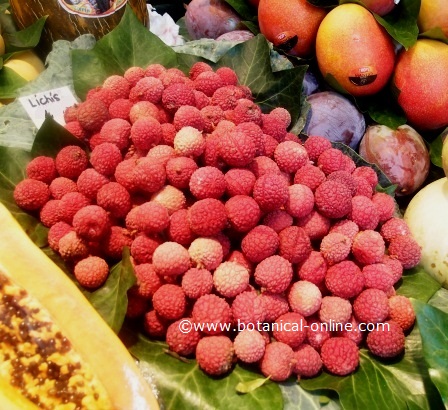
 In the image: photograph of lychees, as it is sold in a European market.
In the image: photograph of lychees, as it is sold in a European market.
Varieties of lychee
Litchi chinensis var. Chinensis: it is the most commercialized fruit at an international level. Skin characteristically pink with conical protrusions, fruit with fleshy and edible pulp.
Litchi chinensis var. Philippinensis: It is called alupag. Variety present in the Philippines, whose fruits are not edible.
Litchi chinensis var. Javanensis: variety grown in some regions of Indochina and west Java. Edible fruits.
Composition of lychee
Carbohydrates: It contains sugars.
Vitamins: Mainly its content in vitamin C.
Flavonoid glycosides (in seed): in scientific studies, some of these components have shown in vitro antitumor activity: lychidoideD, pinocembrin7Oneohesperidoside, pinocembrin 7Orutinoside, taxifolin 4’OΒDglucopyranoside, kaempferol 7Oneohesperidoside, tamarixetin 3Orutinoside and phlorizin.
Triterpenes: betulinic acid, betulin, lupeol, daucosterol. Some of these components have a protective role against cancer, according to the first scientific studies.
Phytosterols: betasitosterol, stigmasterol.
- Phenolic acids: Gentisic acid, protocatechic acid.
Lychee extract is rich in polyphenols, anthocyanins and flavonoids and has shown a protective role against breast cancer in experimental studies.
Flavonoids (fruit): epicatechin mainly, procyanidin.
Anthocyanins (fruit): cyanidin3rutinoside, cyanidin3glucoside, quercetin3rutinoside and quercetin3glucoside, a type of flavonoids, which function as plant pigments (they provide color to the fruits) with antioxidant activity.
| Composition of lychee per 100g. | |
| Nutrient | Amount |
| Water (g.) | 81,76 |
| Calories (kcal) | 66 |
| Carbohydrates (g.) | 16,53 |
| Protein (g.) | 0,83 |
| Fat (g.) | 0,44 |
| Fiber (g.) | 1,30 |
| Vitamin C (mg.) | 71,50 |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) (mg.) | 0,01 |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) (mg.) | 0,07 |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) (mg.) | 0,60 |
| Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) (mg.) | 0,10 |
| (Folic acid) (mcg.) | 14 |
| Calcium (mg.) | 5 |
| Magnesium (mg.) | 10 |
| Phosphorus (mg.) | 31 |
| Sodium (mg.) | 1 |
| Potassium (mg.) | 171 |
| Iron (mg.) | 0,31 |
| Zinc (mg.) | 0,07 |
| Copper (mg.) | 0,15 |
| Selenium (mcg.) | 0,60 |
![]() More information on lychee.
More information on lychee.









