Contents
What is a parsnip?
Characteristics of parsnip (Pastinaca sativa)
Common English name: Parsnip
– Scientific name: Pastinaca sativa L.
– Etymology: “Pastinaca” from Latin ” pastinaca (= carrot or parsnip) which comes from “pastinum”, a sort of tool to hoe the earth in the garden. “sativa” comes from latin “sativus” (=cultivated)
– Taxonomic synonyms: P. pratensis (Pers.) H.Mart; P. sylvestris; P.umbrosa; P. opaca…
* See: Parsnip in other languages
– Family: Apiaceae (Umbelliferae)
– Origin: Plant native to Europe and Asia. It produces an edible aromatic root . In the past, before the introduction of potatoes, parsnips were used in food as a staple food.
Description of parsnip
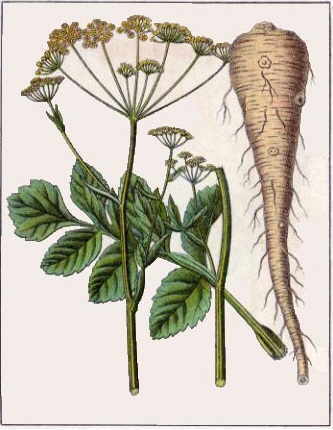
It is a plant belonging to the botanical family of the Umbelliferae (Apiaceae), the same to which other edible plants belong , such as carrots (Daucus carota), celery (Apium graveolens), coriander (Coriandrum sativum) , parsley (Petroselim crispum) or fennel (Foeniculum vulgare).
This plant is biennial in cycle: it develops a thickened root with cream-colored skin and white flesh, reminiscent of a discolored carrot during the first year. So, it acumulates starches in it as a reserve energy source for the following year to develop its flower stems, flowers and fruits.
Its flowers are greenish yellow, gathered in umbels.
History, types and varieties of parsnip
The variety of parsnip that is currently consumed was developed in the Middle Ages. However, it is estimated that the wild parsnip was already consumed by the Romans. Currently, the plant appears naturalized in many regions of Europe, including the entire Mediterranean basin.
The cultivated parsnips are varieties obtained from the wild parsnip (Pastinaca sativa subs. sylvestris), which differs in that it has a hairier stem, is smaller in size, and its root is not as thick.
Where does a parsnip grow?
Wild varieties grow practically throughout Europe along the roads, paths, next to wet ditches or among grasses. Parsnips have been consumed in Europe and Asia for centuries, since, before the introduction of the potato, it was a frequent food in the diet.
Uses of a parsnip root

The root of this plant is characteristically very aromatic, which is why it is used in broths, roasts and preparations to which it provides a remarkable flavor.
It has a slight anise aroma and a spicy touch that make it very peculiar. The aromas of this plant give it very satiating properties.
Winter parsnips taste sweeter than fall parsnips, because the cold causes the plant to transform its starches into sugars. In the past, these were used in the United Kingdom to make jams, cakes and other sweets.
Differences between a parsnip and a carrot
Parsnips and carrots are two very similar roots that belong to the same botanical family, but they should not be confused. Its flavor is very different, because a parsnip is more aromatic and fibrous than a carrot.
Some people mistakenly believe that parsnip is a type of yellow carrot, which is false and is denied in the image above.
![]() More information on parsnip
More information on parsnip








