Contents
Nitrosamines in food
What are nitrosamines?

Nitrosamines are carcinogenic compounds present in foods that are formed from nitrites. Nitrites pass to nitrosamines during the cooking, curing or salting of meat, or by the action of the intestinal flora during digestion.
Foods that contain nitrites are mostly processed meats, precooked foods and other industrial products.
Nitrites can also be formed from nitrates, present in meats and also in vegetables.
The most abundant type of nitrosamine is n-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA).
These compounds are absorbed by respiratory, skin and digestive tract.
Foods with nitrates and nitrites
Nitrates and nitrites reach our food because they are used in nitrogen fertilizers and animal manure to fertilize plants.
These substances pass to the soil and thus to vegetable foods. They come to our body through diet (food or food additives), water and also cosmetic products.
Nitrite and nitrate additives
Nitrites and nitrates are additives used to preserve the color of meat foods and protect them against the attack of bacteria. Nitrites or nitrates can be found in processed meats such as sausages, cold meats, anchovies, pates and preserves.
They are used to prevent the growth of microorganisms and the deterioration of the color of meat foods, so that they retain their red color.
Nitrites are transformed into carcinogenic nitrosamines

The conversion of nitrites to carcinogenic nitrosamines occurs slowly. In refrigerated foods, this process is slower. During the cooking of the food, the temperature increases nitrosamine formation.
The microbiota or intestinal flora can also convert nitrates and nitrites into nitrosamines. The longer food with nitrites or nitrates (mainly meats) remain inside the intestine, the greater the amount of these carcinogenic compounds will form. For this reason avoiding constipation reduces the formation of nitrosamines in the body.
It is one of the reasons why a diet rich in fiber reduces the incidence of colon cancer, by causing evacuation and prevent the formation of these components in the digestive tract.
Risks to the health of nitrosamines: cancer
Nitrosamines increase the risk of cancer of the esophagus, stomach, liver, lung and urinary.
It is believed that they are also responsible for some cases of food allergy with manifestations of urticaria.
Toxicity and dangers of nitrosamines

The toxicity of nitrosamines is due to their habitual presence in the diet.
Scientific studies have shown that nitrosamines are toxic in large doses (which are not usually found in food) or in small amounts to repeated doses for a long time.
For this reason, one of the most important public health problems today is the excessive consumption of processed meat. You should not eat foods rich in nitrosamines usually, through, for example, processed meats such as bacon, hamburgers, cooked ham, sausage, barbecues, smoked or cured meats.
- Children are more sensitive to nitrosamines, so these should be found less in their diet than in the diet of adults.
* See: How to replace processed meat
How to prevent the formation of harmful nitrosamines?
When consuming barbecues, processed meats or other foods rich in nitrites, it is recommended that these be accompanied by aromatic herbs, spices, crude oils (cold pressure), fruits and vegetables.
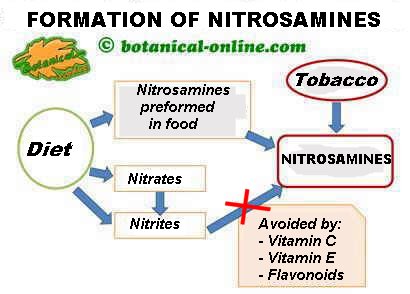
The transformation of nitrites to nitrosamines is slowed by the presence of vitamin C, vitamin E and flavonoids, nutrients present in these foods.
Nutrient deficits aggravate the toxicity of nitrosamines. It has been shown that the lack of vitamin A (present in brightly colored fruits and vegetables) and zinc (present in legumes and whole grains) increases their carcinogenic effect.
The consumption of alcohol enhances the carcinogenic effects of nitrosamines.
Tobacco is a source of nitrosamines, in addition to other carcinogens.
![]() More information on nitrosamines and other toxic products
More information on nitrosamines and other toxic products
23 April, 2019