Contents
- 1 Pectin in apples provides soluble fiber, a solution against cholesterol and diabetes
- 1.1 Why do apples diminish cholesterol?
- 1.2 Soluble fiber properties
- 1.3 APPLE NUTRIENT CONTENT
- 1.4 Why do apples are good for people with diabetes?
- 1.5 Apples with skin and peeled apples: Advantages and drawbacks
- 1.6 Quercetin in apples, an antidote against cancer and heart disease
- 1.7 Apples help keep the intestines and the body in generally good condition
- 1.8 Apple side effects
Pectin in apples provides soluble fiber, a solution against cholesterol and diabetes
Why do apples diminish cholesterol?
Apples are noted for their richness in pectin. Pectin is a soluble fiber. Is part of the cell wall of plants, particularly in fruit skins. Pectin is capable of forming a gel when combined with sugar or with acids, which is used by the industry in making jams.
Among all plants, marshmallow is containing the highest pectin levels. Carrots would be the richest vegetable along with eggplants, pumpkins, potatoes, or tomatoes. Apples are the richest fruits.
Other fruits that contain much soluble fiber are figs, bananas, pears, plums, oranges or strawberries.
Legumes are also rich in this component, peas and beans standing among all of them. Oats and corn stand out among cereals.
Soluble fiber properties
Soluble fiber helps to lower cholesterol levels in the blood. This type of fiber prevents re-absorption of intestinal cholesterol to bile produced by the digestion of the food. Soluble fiber forms a gel that traps the cholesterol that is discharged to the outside without going into the blood stream. The liver needs cholesterol to form fatty acids, it needs to take from blood which leads to a cholesterol decrease.
Reducing cholesterol level conveys a reduction of risk of vascular accidents. It has been found that eating foods rich in soluble fiber lowers cholesterol levels up to 10%. Most natural plant foods are rich in soluble fiber. Eating apples is usually a good way to control cholesterol.
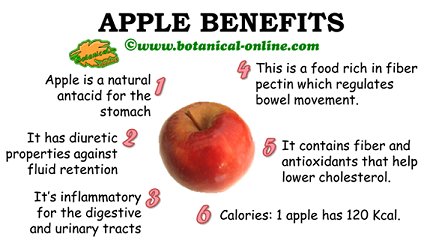
Main healing properties of apples
APPLE NUTRIENT CONTENT
Main nutritional components of apples
| Composition of apples per 100g | |||
| Nutrients | Raw with skin | Raw peeled | Boiled peeled |
| Water | 83, 9 gr. | 84,4 gr. | 85,47 gr. |
| Calories | 59 Kcal | 57 gr. | 53 gr. |
| Fat | 0, 36 gr. | 0, 31 gr. | 0, 36 gr. |
| Proteins | 0, 19 gr. | 0,15 gr. | 0,26 gr. |
| Carbohydrates | 15, 25 gr. | 14, 84 gr. | 13, 64 gr. |
| Fiber | 2,7 gr. | 1,9 gr. | 2,4 gr. |
| Potassium | 115 mg | 113 mg | 88 mg |
| Phosphorus | 7 mg | 7 mg | 8 mg |
| Iron | 0, 18 mg | 0, 07 mg | 0, 19 mg |
| Sodium | 0 mg | 0 mg | 1 mg |
| Magnesium | 5 mg | 3 mg | 3 mg |
| Manganese | 0, 045 mg | 0, 023 mg | 0, 35 mg |
| Selenium | 0,3 mg | 0,3 mg | 0,3 mg |
| Zinc | 0, 04 mg | 0, 04 mg | 0, 04 mg |
| Copper | 0,041 mg | 0,031 mg | 0,035 mg |
| Calcium | 7 mg | 4 mg | 5 mg |
| Vitamin C | 5,7 mg | 4 mg | 0,2 mg |
| Vitamin E | 0,320 mg | 0,080 mg | 0,010 mg |
| Vitamin A | 53 UI | 44 UI | 44 UI |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) | 0, 017 mg. | 0, 017 mg. | 0, 016 mg. |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 0, 014 mg | 0, 010 mg | 0, 012 mg |
| Folic acid | 4 mg | 0 mg | 1 mg |
| Niacin | 0, 077 mg | 0, 091 mg | 0, 095 mg |
Why do apples are good for people with diabetes?
In addition to lowering cholesterol, the intake of fiber-rich foods helps stabilize blood sugar levels, so that fiber is suitable for feeding patients with diabetes. Fiber slows the absorption of carbohydrates so it helps reduce the typical “ups ” of blood sugar in people with diabetes.
Texas studies demonstrated that a daily ingestion of 25 gr. of soluble fiber besides 25 gr of insoluble fiber served to positively regulate sugar levels in a group of diabetic patients. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends lower figures for the same purpose (26 gr. of insoluble fiber daily and 8 gr of soluble fiber ) A medium apple provides about 2 gr. soluble fiber.
Apples with skin and peeled apples: Advantages and drawbacks
Fruits usually have to be eaten with their skin. This is especially interesting in the case of apples. We should keep in mind that a lot of soluble fiber is found in the skin, making it convenient to eat unpeeled apples.
This is only possible provided that they are properly clean and grown from biological sources, where neither pesticides have been used nor have been subjected to a beautification process before hitting the market. Waxes, polishes, color enhancers or other products are generally employed to enhance their appearance and improve sales.
If you are not sure that a fruit comes from reliable sources, it is best to peel it because the negative effects of these substances can be counterproductive to the benefits that consumption of the skin can offer.
Unfortunately, the loss of the skin, as seen in the right table on the composition of this fruit, along with a loss of fiber, conveys a lower intake of vitamins and minerals.
Quercetin in apples, an antidote against cancer and heart disease
In addition to soluble fiber, apple has another very important component: quercetin. Quercetin is a flavonoid that is a natural dye, with many properties. Among all of them, its antioxidant capacity, that is to say, its capacity to neutralize free radicals, particles that oxidize the body and are able to predispose us to the occurrence of many diseases.
It was found that quercetin, given as supplements in doses of 200 to 1100mg per day, is capable of preventing the formation of cancerous tumors, especially tumors of the bladder caused by tobacco smoke f. The problem is that quercetin supplements present some contraindications and they often have some side effects.
We have other resources to ingest this component in a natural way. We can choose eating lots of onions, which are the richest food, using oats, or eating apples which are the richest fruit in quercetin and the third food after onions and oats. There is an even better opportunity to combine oats with apple for breakfast. We can prepare a rich muesli with these two foods, along with yogurt, honey and raisins that will provide all the benefits of a natural, healthy food. (See recipe for muesli)
Quercetin, among its many properties, also plays an important role in reducing the ” Bad cholesterol ” or LDL to prevent oxidation of the “good cholesterol ” or HDL. From a point of view of health, the fact that this component prevents this transformation is of great advantage in protecting against cardiovascular disease. We all know the great importance that high cholesterol has on the health of the arteries and heart. Taking quercetin, or eating plenty of foods rich in this component helps reduce “bad cholesterol ” in the blood so it protects our body from the appearance of thrombi in the arteries responsible for diseases like atherosclerosis, angina pectoris or myocardial infarctions.
Apples help keep the intestines and the body in generally good condition
Apples regulate intestinal activity. First, they have a laxative effect, produced by its richness in fiber, sulfur, fructose and sorbitol. Moreover, the content of zinc or gallic acid has astringent properties. All this helps to regulate bowel movements being able to stop diarrhea or ” loosen ” the intestines in constipation sufferers.
We must not forget that malic acid and quercetin possess bacteriostatic properties,so, they are able to inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria responsible for many cases of intestinal putrefaction that causes gases, indigestion, colitis, etc..
Moreover, apples especially contain vitamin C and potassium. Vitamin C helps to reinforce the antioxidant bioflavonoids by means of protecting them from oxidation. Without being too rich in vitamins, at least, vitamins in apples do not break down so much as in other plants once the fruit has been picked from the tree. Vitamin C is lost practically when the apples are cooked, as you can see in the table above.
Being abundant in potassium, apples facilitate diuresis which makes them suitable for fluid retention diet and for weight loss diets.
Finally, we have to consider apple a good natural toothpaste, because of its bacteriostatic properties. A piece of apple after dinner, will clean the mouth and will protect it against the development of harmful bacteria of caries or gingivitis .
Apple side effects
It is worth to say that apples contain in its composition a very high amount of gases which, if we do not eat this food properly, may be responsible for flatulence. Eating apples can greatly increase the gas content in the intestines,
However, if we do not eat apples, we will be discarding one of the richest foods in pectin, a type of highly recommended fiber to avoid constipation. The best thing to do is to eat this food slowly, chewing it well to allow time for internal gases of apple to be expelled from the mouth before swallowing them.
![]() More information on apples.
More information on apples.








