Contents
- 1 How to replace olive oil?
- 1.1 What oils can be taken instead of olive oil?
- 1.2 Why is olive oil so good?
- 1.3 How should a healthy oil be?
- 1.4 Oils rich in monounsaturated fats are recommended
- 1.5 Good olive substitute oils
- 1.6 Low in polyunsaturated fats
- 1.7 So, are seed oils bad?
- 1.8 Search for oils without saturated fats
- 1.9 Is it a good solution to substitute olive oil by coconut oil?
- 1.10 What about replacing olive oil by moringa oil?
- 2 OLIVE OIL SUBSTITUTES AND DIFFERENCES
- 3 Best vegetable oils to replace olive oil
How to replace olive oil?
What oils can be taken instead of olive oil?

Although olive is considered one of the healthiest types of oil in the world, it is not available in all countries of the world, and therefore many people look for other healthy alternatives to this oil.
Why is olive oil so good?
The benefits of olive oil, the emblem of the Mediterranean diet, are due to the fact that it is rich in oleic acid, has a balanced ratio in omega 3 and 6. In addition, olive oil of good quality (virgin and cold pressure) ) provide a lot of vitamin E and polyphenols, with antioxidant and heart-healthy properties.
- A good substitute should have characteristics similar to virgin olive oil: be rich in oleic acid and vitamin E.
How should a healthy oil be?
>> An oil without trans fats, not refined and obtained by cold pressure.
The basic characteristics desirable for an oil are that they are not refined and that they are obtained by mechanical procedures (without heating or solvents). These are the so-called “virgin oils or obtained by cold pressure“, which conserve better their healthy fats and all their antioxidants.
Refined oils are not recommended because during refining the oils lose a large part of the vitamins and antioxidants (polyphenols, responsible for the taste of the oil).
In addition, during this refining process, the fats in the oil lose their properties. Refined oils have higher acidity, indicating deterioration of fats (the higher the degree of acidity, the more oxidized that oil is).

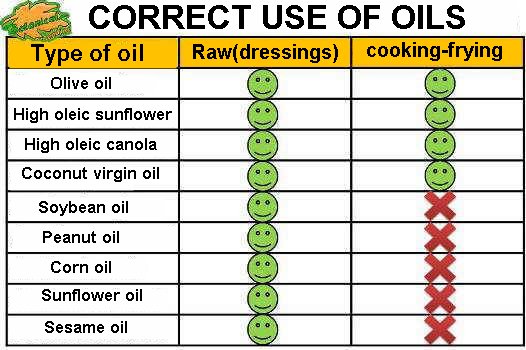
- All the oils that are consumed should be unrefined, both for salad dressings and for cooking.
- Occasionally a high oleic oil (with added vitamin E) can be used for frying, but in general it should not be eaten fried regularly.
Oils rich in monounsaturated fats are recommended
An oil rich in monounsaturated fats is desired, such as omega 9 oleic acid which you can find in olive oil, canola oil, hazelnut oil and avocado oil.
Monounsaturated fatty acids are more stable and resist heat and oxidation better (by light, contact with oxygen, etc.). For this reason, they constitute a good foundation to form new cells of our body, besides being the most suitable for cooking (more resistant to temperature).

Good olive substitute oils
Olive oil contains more than 70% monounsaturated fats, responsible for much of its benefits.
The following oil types are rich in monounsaturated fatty acids, and, therefore, good substitutes for olive oil:
- High oleic sunflower oil (84% monounsaturated fatty acids, “omega 9”)
- Hazelnut oil (78%)
- High oleic canola oil (75%)
- Moringa oil (70%)
- Avocado oil (70%)
- Edible almond oil (70%)
- Canola oil (60%)
- Macadamia oil (60%)
Low in polyunsaturated fats

The high content of polyunsaturated fats is the main problem of seed oils, such as sesame oil, walnut oil or sunflower oil, because this type of fats deteriorate easily generating free radicals in the body.
It may seem like a contradiction, but omega 3 and omega 6 are very harmful when used for frying.
The reason is that polyunsaturated fats deteriorate (smoke) quickly with cooking, since their structure is more unstable, so they do not resist high temperatures . This causes that many free radicals are generated, causing problems such as the increase of bad cholesterol or premature aging.
Many studies warn about the negative effects of these fried oils of poor quality.
In addition, cooking with this type of oils provides a lot of omega 6 that blocks the benefits of omega 3.
In general, all seed oils (sunflower, sesame, walnuts, etc.) are very rich in omega 6 and should be consumed with a lot of control so as not to overdo it.
As an omega source, it is better to consume foods rich in omega 3 (flax, chia, hemp seeds, nuts or sesame) than oil (flaxseed oil, walnuts or sesame oil).
So, are seed oils bad?
This does not mean to completely eliminate the seed oils.
The first cold pressed seeds oils (not refined) are healthy, because they provide omega 6 of good quality, along with antioxidant vitamin E. It is recommended to use these oils in dressings, salads and raw recipes.
- As sources of omega 3 and omega 6 it is better to consume foods rich in omega (flax, chia, hemp seeds, walnuts or sesame) than oils rich in these fatty acids (flaxseed oil, walnut oil or sesame oil) .
Search for oils without saturated fats
Palm oil is never recommended because of its high content of palmitic acid, a type of long chain fatty acid that compromises the health of the heart by increasing bad cholesterol, and being inflammatory and atherogenic.
The most common way to find these oils is in processed foods (chocolates, pasta, etc.) and in their hydrogenated form, presenting trans fats harmful to health. Margarine or vegetable butters also usually contain hydrogenated or trans fats, or many additives, so in no case are they advisable.
Saturated fats are those that abound in animal fats such as butter or lard (sausages, sausages, …). In general, all vegetable oils are poor in this type of fat, with the exception of coconut oil and palm oil.
Is it a good solution to substitute olive oil by coconut oil?
No, coconut oil is no more advisable than olive oil, so in countries where olive oil is available at an affordable price, it is better to consume good quality olive oil than virgin coconut oil (olive oil pressure in cold).
It is increasingly common to hear about the benefits of coconut oil, which is rich in lauric acid, a medium-chain fatty acid that has not shown atherogenic effects. If this option is used, a virgin coconut oil should be recommended, and in moderate amounts.
Olive oil is better because it has shown the greatest benefits in studies and has a large amount of flavonoids and antioxidant vitamins. Virgin coconut oil may be an option to replace it, in countries where there is no olive oil at an affordable price.
What about replacing olive oil by moringa oil?
Moringa oil is one of those that could potentially replace olive oil in climates where it is not possible to grow. It is a tropical tree whose seeds you can extract an oil rich in omega 9. There are varieties whose percentage can rise to 80% omega 9, like olive. This makes it a promising oil.https://www.botanical-online.com/en/food/moringa-olive-oil
In addition, moringa also uses other parts of the plant for medicinal purposes, mainly to lose weight and to treat cancer.
* More information: Comparison of moringa and olive oil
OLIVE OIL SUBSTITUTES AND DIFFERENCES
Unfortunately, olive oil can be an unavailable product, especially outside Europe, the region where it is most grown. But there is no problem in replacing this oil with another cheaper, depending on the country in which we are:

What oil to use for frying?
All oils deteriorate when frying, due to the effect of high temperatures on the chemical structure of fats. Dr. Kousmine already spoke of it when he recommended “not consuming too many heated oils” in our healthy diet.
The oils that best resist the frying temperature are : olive oil, canola oil and high oleic sunflower oil, but in general they should not be eaten fried regularly.
To compensate the fried foods, it is recommended to accompany them with many antioxidants that will help to neutralize the excess of free radicals formed: mango, oranges, tangerines, guava, kiwi, avocado, persimmon, tomatoes, guanabana, etc.
Why is it bad to fry an oil?
When an oil is heated a lot, toxic compounds are formed, such as acrolein, pre-oxides or PAHs. For this reason it is not advisable to use a lot of oil and, specially, very hot (such as frying temperatures) in cooking.
- Seed oils are not suitable for frying (except high oleic)
- The healthiest thing is to use these oils of first pressure in cold and raw, or cooked at mild temperatures, in salads and healthy recipes.
Avocado, the American olive
Avocado is the fruit with a profile and quality of fats very similar to that of olives, so it is considered one of the best and healthiest options to replace olive oil.
It has a balanced fat profile, plus plenty of vitamin E and fiber. It can be used in the form of virgin oil or directly the fruit (which will be even more tasty and nutritious). We will obtain its benefits by adding it in salads and sauces as one more ingredient.
Homemade guacamole sauce is an excellent mayonnaise, better than sauces made with refined or poor quality seed oils
Best vegetable oils to replace olive oil
High oleic vegetable oils
After olive oil and hazelnut oil, which can be difficult to find, canola or high oleic sunflower oils are undoubtedly the most advisable options for cooking or frying, because they resist the cooking temperatures well. When infused “high oleic” usually means that seeds are usually modified to contain more omega 9. Many times they are added vitamin E.
Canola oil that is not high oleic maintains a good amount of omega 9 and would also be adequate. Normal sunflower oil does not have these properties, but on the contrary, smokes easily and is not suitable for frying or cooking.
Many times these oils are refined (they have lost their vitamin E), so it is recommended to choose high oleic oils and enriched in vitamin E or first pressing because they are more rich in vitamins.
- People with cholesterol, hypertension or diabetes should use this type of oil and not use soy, corn or peanut oil, as they are too rich in polyunsaturated fats.
Are unrefined seed oils good to cook?

No. In general, it is best to use oils of quality seeds and raw, and accompany them with abundant antioxidant foods, mainly fruits and vegetables: Carrots, pumpkin, apples, pear, fruit compote, baked apples, bananas, medlars, mango, chayotes, zucchini, quince,seaweed, etc.
- Sunflower oil not refined: Sunflower oil not refined cold pressure is highly recommended for its contribution in vitamin E and omega 6 essential fatty acids. It is one of the most economical oil prices, among the unrefined. It should be consumed raw, in dressings. As mentioned, the seed oils are not suitable for cooking.
- Sesame oil: It is a good option to use raw, it is very rich in omega 6. We can use it to season, although for a similar or even cheaper price, olive oil offers greater benefits. Buy only the one obtained from cold pressure.
Other oils not recommended for cooking
- Corn oil: In general, it is not recommended for frying or cooking. It has a low content of monounsaturated fats (30%) that do not make it suitable for cooking. And to dress salads, soy oil is better because it contains more omega 3.
- Soybean oil: Soybean oil is not suitable for frying because it smokes easily. This is because it is very rich in polyunsaturated fats (58%) and very poor in monounsaturated (23%). It differs from all other oils because it is the richest in omega 3, which makes it suitable for seasoning dishes. The main problem is that it comes from refined and poor quality oils.
- Peanut oil: It is not considered a good option since it does not contain omega 3, although it has better frying properties than soy or corn oil. In case of using it in the diet, it is necessary to consider eating foods rich in omega 3. Only the virgin is recommended, obtained from first cold pressure or unrefined oils, but it usually has a very high price.
- Argan oil: Argan oil is one of the fruits with composition more similar to the olive, which can be consumed in some regions of Morocco. It is suitable for cooking and dressing, which provides a delicate aroma of hazelnut. But outside its region of origin is an oil difficult to find and the region where it is produced is protected, so its consumption is not sustainable.
How to get enough omega 3 and omega 6?
In general, food based on sunflower, soybean or corn oil provides excess omega 6 polyunsaturated fats, which blocks the anti-inflammatory benefits of omega 3 by competing for the same metabolic pathways.
Therefore, oil should be compensated by taking more omega 3, such as two tablespoons of ground flax seeds, or the same amount of chia seeds daily.
The following healthy diet tips are recommended:

- Reduce the amount of oil used for cooking. Avoid the fried ones. In exchange for reducing the oil, we can add avocado or nuts and seeds to salads, sandwiches, etc.
- Add seasonings rich in vitamin C as half lemon squeezed to the dishes
- Increase foods with omega 3, such as quinoa, walnuts, chia, flaxseed or hemp seeds. All these foods should not be lacking in salads, mixed with yogurt or as a complement in all kinds of preparations in general.
- Cook or fry with olive oil or, failing that, with canola or high oleic sunflower oil. Among the other types of oils, frying will always choose the oil richest in monounsaturated fats.
It is recommended to go to a qualified dietitian for advice.
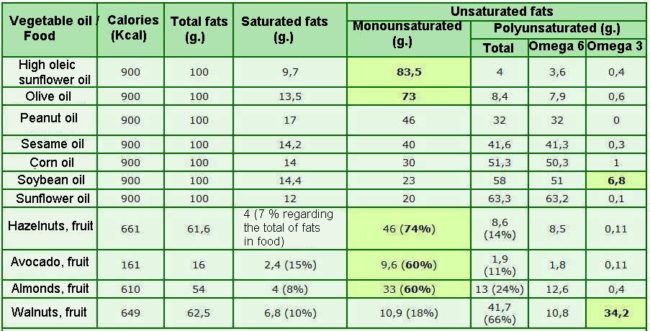
Table of composition of oils and rich food in fats for order of higher to less content in monounsaturated fats.
![]() More information on oils.
More information on oils.








